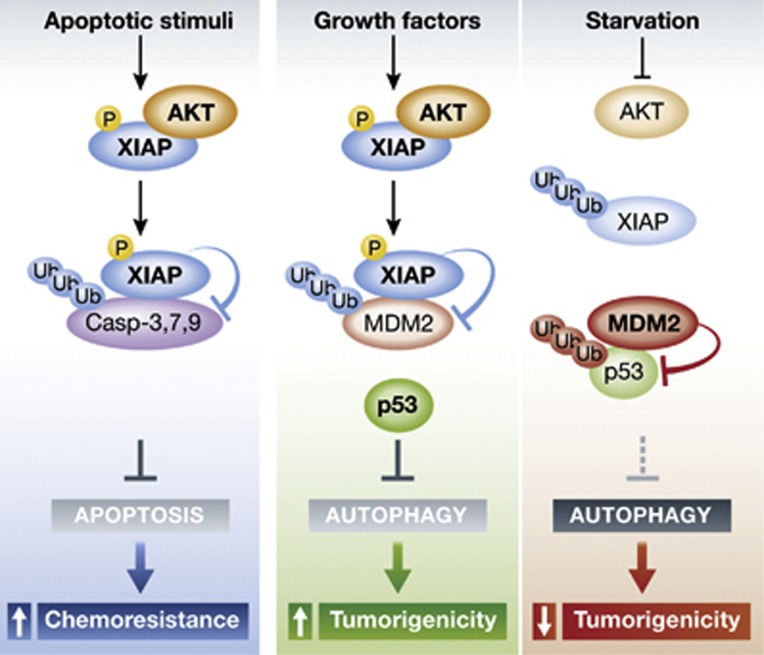
Figure 1.
Following a range of apoptotic stimuli, XIAP is phosphorylated by Akt. This modification leads to its stabilization and promotes XIAP-dependent proteosomal degradation of caspases 3, 7 and 9. The result is a block of apoptosis and tumour chemoresistance. Under unstressed conditions, XIAP is phosphorylated by Akt as well, but targets Mdm2 for degradation. This causes the stabilization of cytoplasmic p53 and can inhibit autophagy. Starvation, on the other hand, inhibits Akt and unphosphorylated XIAP undergoes autoubiquitylation and degradation via the proteasome. Subsequently, Mdm2 is stabilized and induces p53 degradation, releasing the block on autophagy.