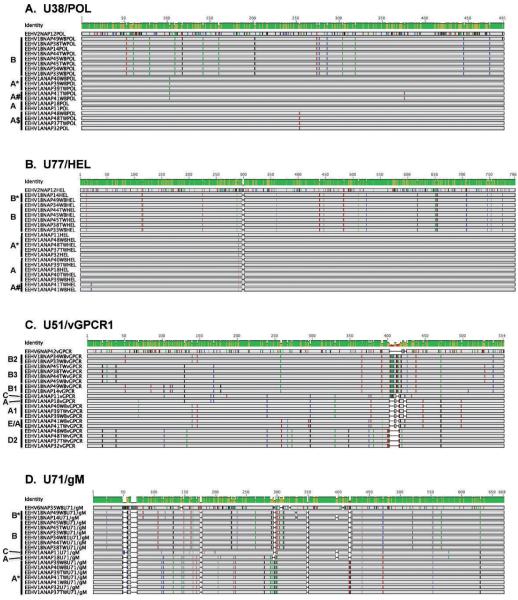
Figure 2.
Graphical presentations showing the nucleotide polymorphisms, genetic relatedness, and subtype patterns of all of the various North American Proboscivirus (NAP) cases studied here at four EEHV genomic PCR loci. Comparisons are made with representative standard prototype strains of EEHV1A (NAP11, 18), EEHV1B (NAP14), EEHV2 (NAP12), or EEHV6 (NAP35, 42) where appropriate (GenBank accession numbers are listed below). (A) The four genetic loci involved are highly conserved DNA polymerase locus (U38/POL). EEHV1A (NAP11) = HM568510, EEHV1B (NAP18) = HM568523, EEHV1B (NAP14) = HM568536, EEHV2 (NAP12) = HM568563. (B) Highly conserved helicase locus (U77/HEL). EEHV1A (NAP11) = HM568515, EEHV1A(NAP18) = HM568529, EEHV1B(NAP14) = HM568542, EEHV2(NAP12) = HM568564. (C) Variable viral G-protein–coupled receptor 1 locus (U51/vGPCR1). EEHV1A(NAP11) = GU350757, EEHV1A(NAP18) = GU350758, EEHV1B(NAP14) = GU350759, EEHV6(NAP42) = JN633926. (D) Variable intergenic myristylated tegument plus glycoprotein-M locus (U71/gM). EEHV1A(NAP11) = GU350764, EEHV1A(NAP18) = GU350750, EEHV1B(NAP14) = GU350767, EEHV6(NAP35) = JN913124. Substitutions from the consensus sequences are color coded (A = green, C = blue, G = black, T = red), and deletions are shown as gaps. Brackets to the left of the alignments indicate the specific gene subtype clusters assigned to the grouped cases based on the previously determined nomenclature system for 35 EEHV1 strains from cases of elephant hemorrhagic disease (Zong, unpubl. data). Cases NAP37, 38, 44, and 45 occurred at the Houston Zoo, Inc.; cases 33, 34, 39, and 40 occurred at the Saint Louis Zoo; and cases 41 and 49 occurred at Feld Entertainment. TW = trunk wash samples; WB = whole blood samples; others including NAP32 (accessions JF692760, GU350766, GU350760, JN633911) at the Houston Zoo in 2007 = necropsy tissue samples.