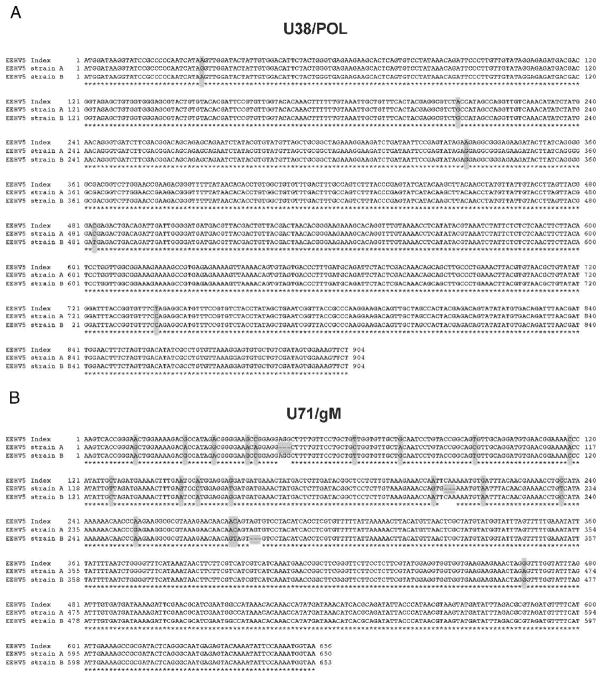
Figure 3.
Sequence comparison between the elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus 5 (EEHV5) index case and two new strains. A. Sequence comparison of 904 base pairs (bp) from the index case DNA polymerase gene (U38/ POL) (see GenBank accession number JN983100), to the same locus from EEHV5 strain A found in elephants 1 and 3–6 (GenBank accession number JN983108.1) and EEHV5 strain B found in elephants 2 and 7 (GenBank accession number JX011012). B. Sequence comparison of 656 bp from the index case glycoprotein M gene (U71/ gM) (see GenBank accession number JN983105), to the same locus from EEHV5 strain A found in elephants 1 and 3–6 (GenBank accession number JN983113.1) and EEHV5 strain B found in elephants 2 and 7 (GenBank accession number JX011021). Sequences were aligned using ClustalW. Asterisks below the sequences indicate sequence identity. Bases highlighted in gray indicate sequence differences or deletions. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) sequencing primers used for the U71/gM locus were the same as those used previously for EEHV1 strains,10 whereas those for the U38/POL locus were specific for EEHV5.4