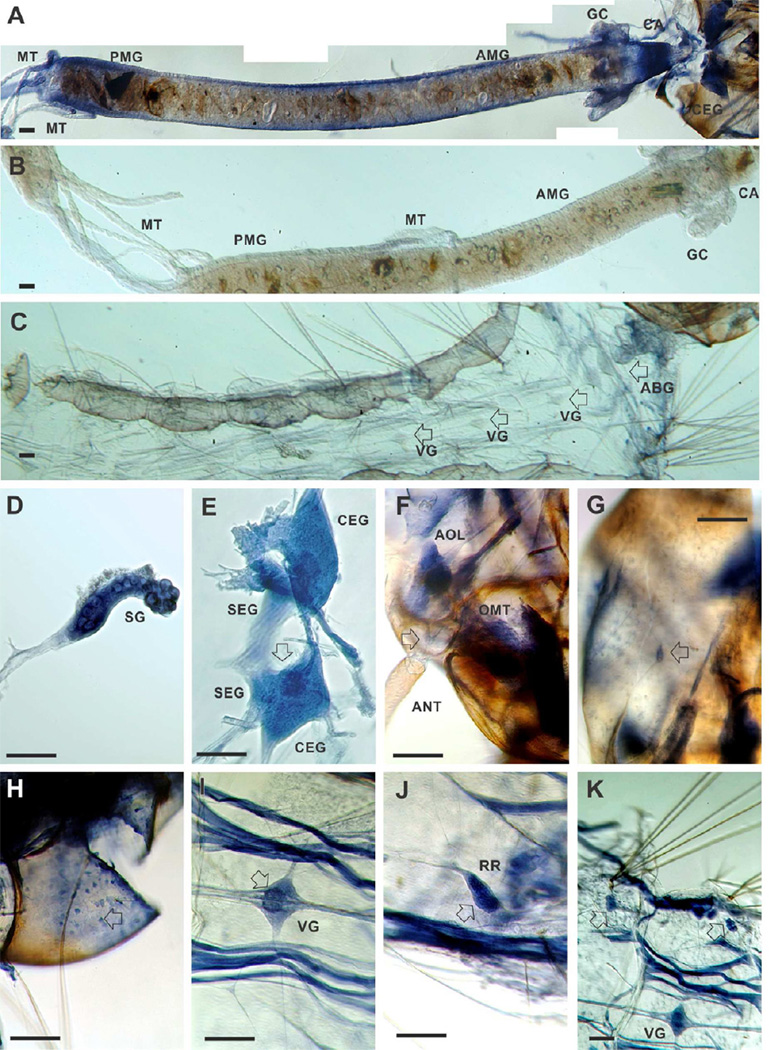
Figure 7. In situ hybridization of AeNAT5 in whole mount preparations of Ae. aegypti larvae.
Labeling was performed in integrated preparations while photographed fragments were isolated for picture clarity. A. High resolution panoramic stitching reconstruction of the larval head and alimentary canal isolated from integument. B and C are representative panels of the isolated gut and integument that were treated equally to the experimental preparation except for using an EGFP antisense probe. D. Isolated salivary gland. E. Cerebral ganglia of the larval central nervous system; arrow indicates upper ocelli projections in the neuropile. F. A high magnification image of a head fragment prepared from a stack of different focal plane images using high dynamic range image fusion techniques, arrow indicates the cluster of olfactory neurons with dendrites projected in to the antenna. G. Labeling in a putative mechanosensory neuron in the larval head capsule (arrow). H. A plexus of multipolar neuronal cells lining the internal surface of the larval head capsule. I. Example labeling of the visceral ganglia; a visceral ganglion of 4th segment is shown; the arrow indicates intensified labeling of cells and neuronal branches in the central region. J. Reproductive rudiments (arrow). K. A low magnification image represented relative labeling intensity in the visceral ganglion, striated muscles, and paired clusters of large cells identified in abdominal segments (arrows; see also C for control labeling). Abbreviations indicate: ABG, Abdominal Ganglia; AMG, anterior midgut; ANT, antennae; AOL, Anterior Olfactory Lobe; CA, cardia; CEG, Cerebral Ganglia; GC, gastric caeca; MT, Malpighian tubes; OMT, Ommatidium; PMG, posterior midgut; SEG, Subesophageal Ganglia; SG, salivary gland; RR, Reproductive Rudiments; VG, visceral ganglia. Scale bars are 100 µM.