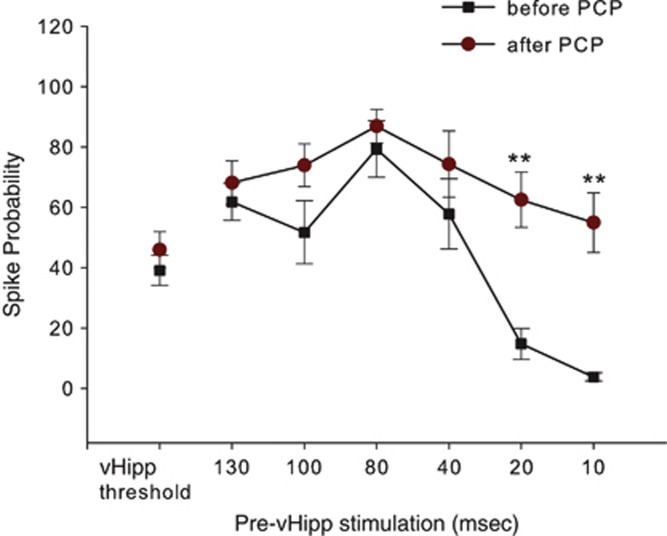
Figure 4.
PCP blocks the inhibitory effect of BLA stimulation on vHipp-evoked activity. PCP administration to normal rats selectively attenuated BLA attenuation of vHipp drive of the mPFC at short ISIs. Administration of the NMDA channel blocker PCP (0.4 mg/kg, i.v.) did not alter vHipp drive of mPFC neurons. PCP administration did not alter the BLA-mediated facilitation of vHipp-evoked spiking in mPFC, whereas it reduced the inhibitory effect of subthreshold BLA stimulation on vHipp-evoked SP in mPFC at short ISIs (**p<0.01 compared with the corresponded ISIs before PCP administration; repeated-measures ANOVA; Tukey's post hoc test).