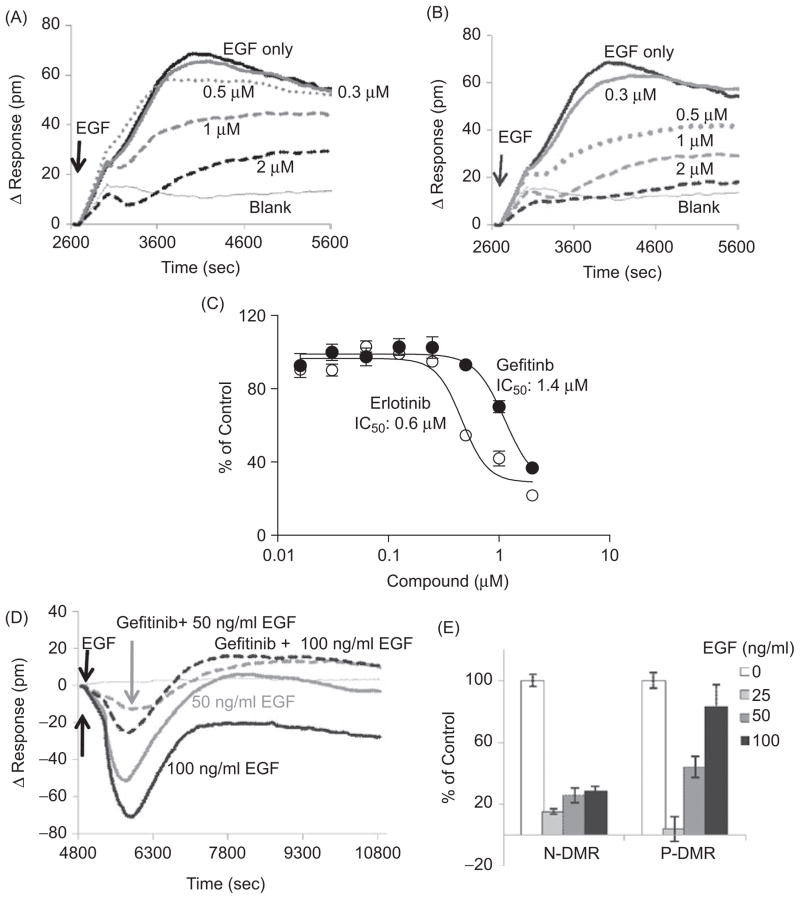
Figure 5.
Validation of the EGF-induced DMR signature assay using gefitinib and erlotinib, two FDA approved drugs targeting EGFR. (A) The effect of gefitinib on EGF-induced DMR response in UPCI-37B SCCHN cancer cells. Increasing concentrations of gefitinib were incubated with the serum-starved cells for 30 min before EGF (100 ng/mL) addition. The DMR signals were then monitored kinetically for 45 min. The real-time DMR response was attenuated dose dependently in the presence of gefitinib. (B) The effect of erlotinib on EGF-induced DMR response in UPCI- 37B SCCHN cancer cells was similar to that of gefitinib. (C) The dose-response curves of gefitinib and erlotinib effects on the P-DMR signal in UPCI-37B cells. The inhibitory effects of gefitinib and erlotinib were normalized to the EGF vehicle control wells without compound, and the IC50 values were calculated by using Prism 4.0 software. (D) The effect of 1 μM gefitinib on DMR response induced by increasing concentrations of EGF in A549 lung cancer cells. (E) The normalized inhibition effect of gefitinib (1 μM) on N-DMR and P-DMR signal in A549 lung cancer cells.