Figure 3. Block diagram of the CLAD system.
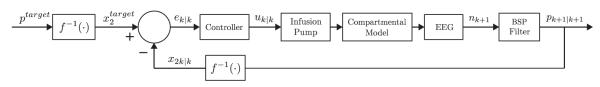
The target level of burst suppression is set by ptarget and is converted into the target brain anesthetic by inverting Eq. (3). The control signal, the current state estimate x2,k∣k computed from the BSP filter in Eq. (9), is subtracted from to compute . The controller uses Eq. (21) to compute the pump’s infusion rate uk∣k. By Eq. (1) the infusion rate changes the anesthetic level in the central compartment and in the brain compartment. Changing the brain compartment level changes the level of burst suppression on the EEG, and hence, the value of the binary time series, nk+1 at time k + 1. The BSP filter uses nk+1 to compute pk+1,k+1, and the update of the control signal x2,k+1∣k+1, which is fed back to compute the next control output uk+1∣k+1.
