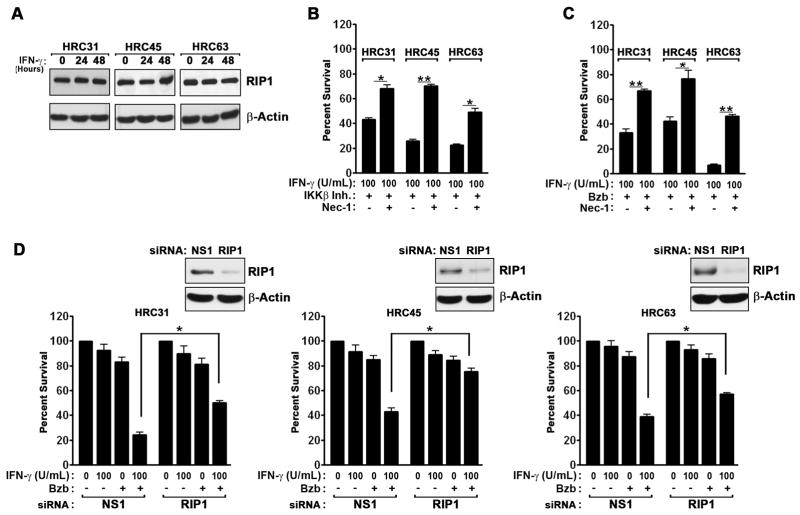
Figure 3. IFN-γ induces RIP1 kinase-dependent necrosis in the presence of IKKβ inhibition or bortezomib.
(A) Immunoblot analysis of RIP1 protein expression in HRC cell lines after IFN-γ (100U/ml) treatment. (B) HRC cell lines were pre-treated with the IKKβ inhibitor IMD-0354 (500 nM) for 1 hr, following which they were exposed to IFN-γ (100U/ml) in the presence or absence of the specific RIP1 kinase inhibitor Necrostatin-1 (Nec-1, 50μM). Cell viability was measured 72 h post IFN-γ treatment. (C) HRC cell lines were pre-treated with bortezomib (MTD) for 1 hr, following which they were exposed to IFN-γ (100U/ml) in the presence or absence Nec-1 (50μM). Cell viability was measured 72 h post IFN-γ treatment. (D) HRC cell lines were transfected with the indicated siRNAs for 24 h, following which they were treated with either IFN-γ (100U/ml), bortezomib (MTD), or the combination of IFN-γ and bortezomib at these doses for a further 48 h, at which time cell viability was measured. Knockdown of RIP1 was confirmed by immunoblotting (inset). Error bars represent mean +/− S.D., n=3. * = p<0.05; ** = p<0.005.