Fig. 4.
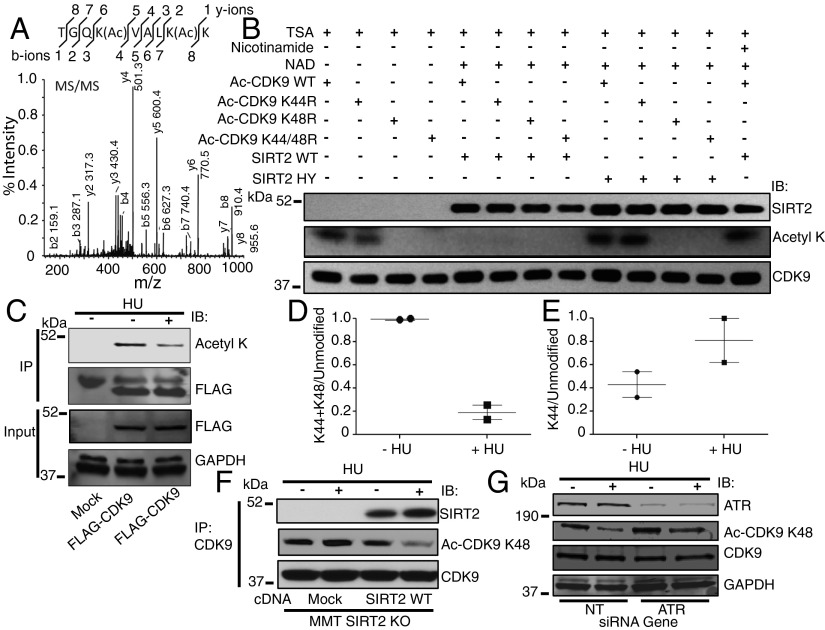
SIRT2 deacetylates CDK9 at lysine residue 48 in response to replication stress. (A) MS/MS peptide spectra of IPed FLAG-CDK9 expressed in 293T cells shows site-specific CDK9 diacetylation at lysine residues 44 and 48. (B) Acetylated CDK9 WT or deacetylated mutants CDK9 K44R, CDK9 K48R, or CDK9 K44/48R was isolated from cells and incubated in an in vitro deacetylation assay with HA-SIRT2 WT or HY in the presence of TSA with or without NAD and nicotinamide. The reaction mixtures were separated by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotted with antibodies against acetyllysine, SIRT2, and CDK9. (C) The 293T cells were transfected with vector or FLAG-CDK9 together with acetyltransferases, treated with or without HU, harvested, IPed with an antibody against FLAG, separated by SDS/PAGE, and immunoblotted with antibodies against acetyllysine, FLAG, and GAPDH. (D and E) Quantitation of acetylated peptide intensities across control and HU-treated samples from C using LC-MS/MS. The propensity of a peptide to ionize, a prerequisite for detection, is dependent on its physicochemical properties such as peptide length, in which representative tryptic peptides have a mass between 600 and 6,000 Da (46). In this study, the expected fully tryptic monoacetyl K48 CDK9 peptide would be only 5 amino acids (K.VALK(Ac)K.V), with an expected mass of 557.39, making this short peptide challenging to detect by LC-MS/MS. However, we were able to observe the double acetylated K44 and K48 peptide and infer that the reduction of this signal after HU treatment was likely driven by deacetylation at K48 specifically because no significant decrease was observed on K44 aceytlation alone (see also Fig. S4 for K44 MS/MS spectra). (F) MMT S2KO cells mock transfected or stably transfected with SIRT2 WT were treated with or without HU, harvested, IPed with an anti-CDK9 antibody, separated by SDS/PAGE, and immunoblotted with antibodies against SIRT2, Ac-CDK9 K48, and CDK9. (G) The 293T cells were transfected with NT or ATR siRNA and treated with or without HU, harvested, separated by SDS/PAGE, and immunoblotted with antibodies against ATR, Ac-CDK9 K48, CDK9, and GAPDH. See also Fig. S4.