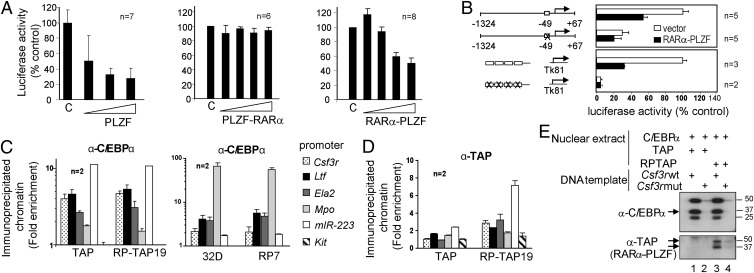
Fig. 3.
RARα-PLZF is recruited to the promoters of C/EBPα target genes in vivo and in vitro via a consensus C/EBP binding site. (A) RARα-PLZF inhibits CSF3R promoter activity in a dose-dependent manner. The 32D cells were electroporated with the CSF3R promoter (−1324 + 67) luciferase construct and increasing amounts of PLZF, PLZF-RARα, or RARα-PLZF expression vectors. Data shown are the means ± SD of n experiments and represent percent of basal CSF3R promoter activity in 32D cells. (B) The C/EBP binding site is necessary and sufficient for transcriptional repression by RARα-PLZF. Wild-type CSF3R promoter construct or a mutant at the C/EBP consensus sequence as well as of a multimer of wild-type or mutated C/EBP binding site constructs were tested in 32D with RARα-PLZF or the empty vector. The basal activity of constructs containing wild-type C/EBPα binding sites were taken as 100%, respectively (average ± SD of n experiments). (C) RARα-PLZF does not affect promoter occupancy by C/EBPα in myeloid cells. Cross-linked chromatin extracts from control cells (32D and TAP) or RARa-PLZF expressing cells (RP7 and RP-TAP19) were subjected to chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) with antibodies against C/EBPα or a control rabbit IgG. Myeloid promoters, amplified by qPCR, are shown as fold enrichment over control IgG and over Hprt promoter sequences (means ± SD of at least two independent experiments done in triplicates). The Kit promoter serves as an additional negative control. (D) RARα-PLZF occupies C/EBPα target promoters in 32D cells, as determined by ChIP with an antibody against the TAP tag or a control rabbit IgG. Data are presented as fold enrichment over control cells transduced with the empty vector (TAP). (E) C/EBPα and RARα-PLZF binding to the Csf3r promoter requires the integrity of the C/EBP binding site. Nuclear extracts (NE) from BOSC cells overexpressing C/EBPα and from 32D overexpressing TAP or RP-TAP were incubated with immobilized wild-type (lanes 1 and 3) or mutated Csf3r (lanes 2 and 4) promoter templates. Bound proteins were revealed by Western blotting.