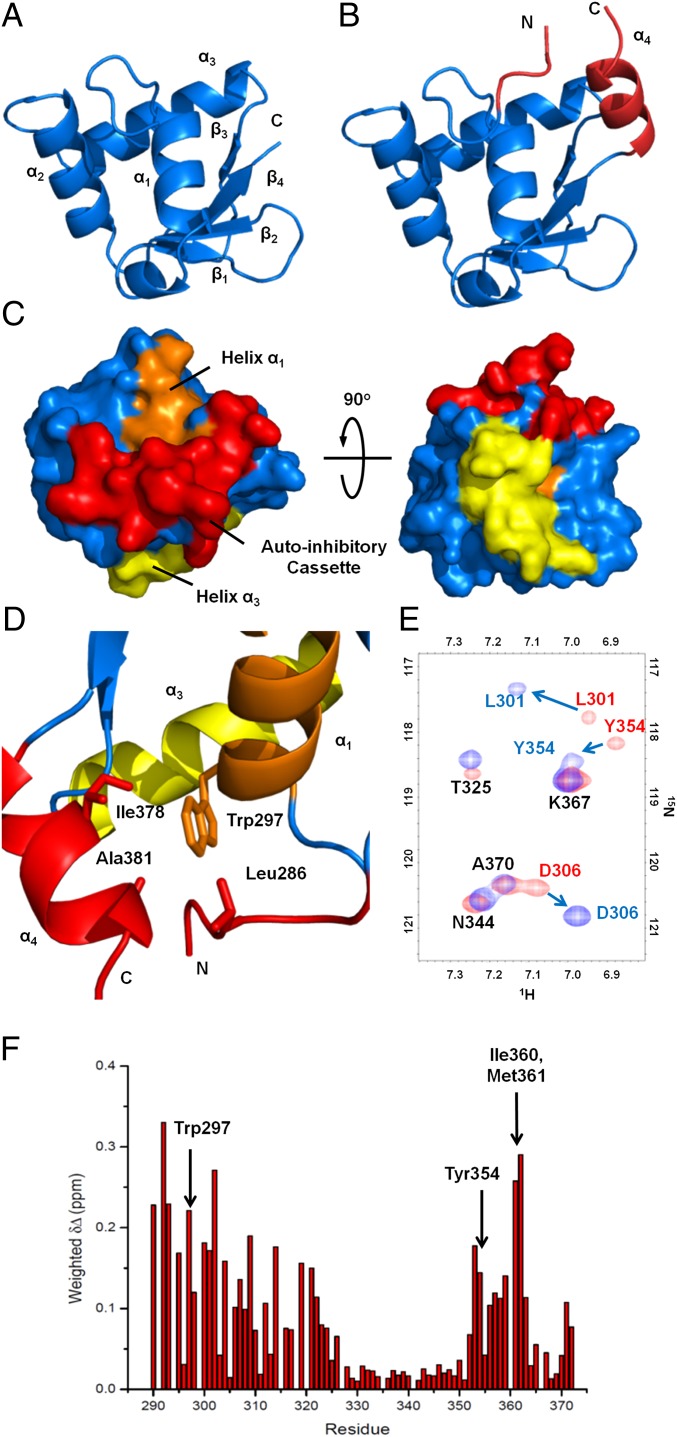
Fig. 3.
Uninhibited and autoinhibited ERG crystal structures and allosteric packing of the autoinhibitory cassette. (A) Structure of the uninhibited ERG Ets domain showing the canonical winged helix-turn-helix fold. For clarity, three N-terminal vector-derived residues and eight C-terminal residues have been omitted. (B) Structure of the autoinhibited ERGi construct, showing the Ets domain with appended autoinhibitory regions in red. (C) Surface representation of ERGi illustrating the packing of the autoinhibitory cassette (red) against helix α1 (orange). DNA-binding helix α3 (yellow) is not obscured by the autoinhibitory cassette. (D) Key residues in the autoinhibitory cassette–Leu286 in the NID, and Ala381 and Ile378 in the CID–pack around Trp297 of the ERG Ets domain. (E) 15N-1H HSQC spectra of 15N-labeled ERGi (blue) and ERGu (red). Residues in ERGi that see large changes from ERGu are labeled in colors corresponding to the respective spectra. (F) Net weighted chemical shift perturbations for residues in ERGu compared with ERGi.