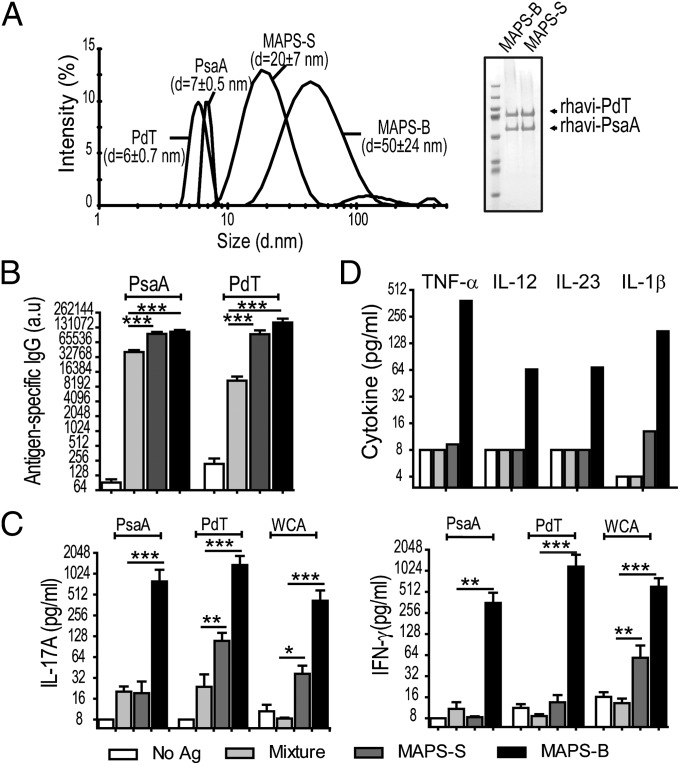
Fig. 4.
Larger MAPS complexes induce significantly greater B- and T-cell immune responses. (A) Small (MAPS-S) and larger MAPS complexes (MAPS-B) were prepared using rhavi-PdT and rhavi-PsaA [in 1:1 ratio (wt/wt)], attached to BD90 or BD500. (Left) The size of MAPS complexes was measured by dynamic light scattering. (Right) SDS/PAGE indicated similar incorporation of both antigens in small and large MAPS complexes. (B) Immunization with small and large MAPS complexes elicited significantly higher antigen-specific antibody responses compared with the uncoupled protein/dextran mixture (mixture). (C) Immunization with larger MAPS complexes, but not small complexes or uncoupled proteins, elicited Th17 (Left) and Th1 (Right) responses against target antigens. Bars represent mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.0001. (D) Stimulation of isolated mouse peritoneal macrophages with larger MAPS complex induced proinflammatory cytokines. Macrophages were stimulated with an uncoupled protein/dextran mixture and small or large MAPS complexes at 1 µg/mL in the presence of aluminum hydroxide (1.2 mg/mL). Cells stimulated with aluminum hydroxide alone (no Ag) served as negative controls.