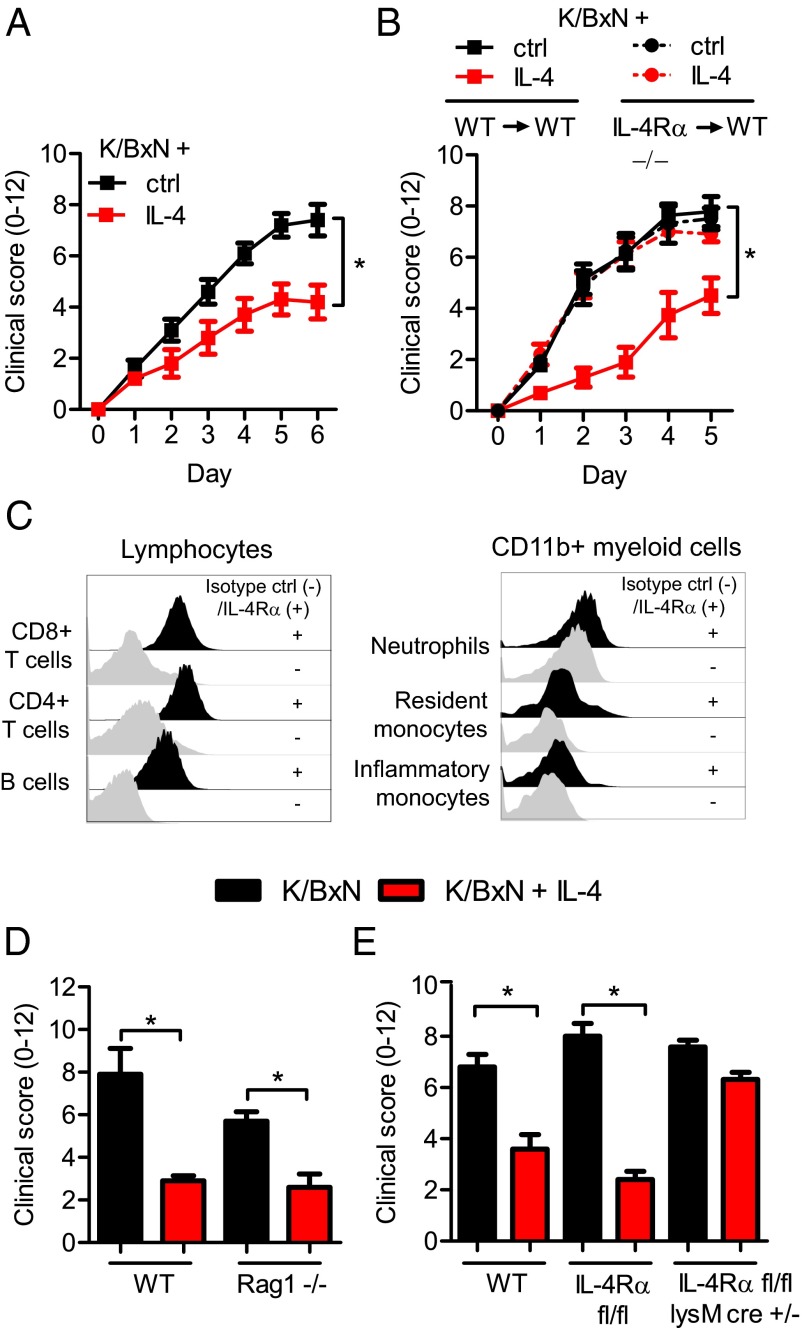
Fig. 1.
IL-4 protects from K/BxN-mediated joint inflammation by targeting IL-4Rα on myeloid cells. (A) WT mice were given K/BxN serum and IL-4 (red) or control (black). Joint swelling (0–12) was followed daily for 6 d and presented as mean and SEM; n = 5 per group. (B) WT mice were irradiated and reconstituted with either WT (WT→WT) or IL-4Rα−/− (IL-4Rα−/−→WT) BM cells. Eight weeks after irradiation and BM transfer, mice were injected with K/BxN serum and IL-4 (red) or control (black). Joint swelling over time is presented as mean and SEM; n = 5–8 per group. (C) Flow cytometry analysis of IL-4Rα expression (black histograms) compared with an isotype control (gray histograms) on major blood cell populations in naïve mice. (D) WT and Rag1−/− injected with K/BxN serum and IL-4 (red) or control (black). Data are shown for day 5 as mean and SEM; n = 5 per group. (E) WT, IL-4Rα fl/fl, and IL-4Rα fl/fl LysMcre+/− mice injected with K/BxN serum and IL-4 (red) or control (black). Data are shown for day 5 as mean and SEM; n = 4–8 per group. *P < 0.05 by Mann–Whitney u test comparing IL-4–treated and control-treated mice at day 6 (A) or 5 (B, D, and E).