Fig. 7. Low numbers of donor CD8+ T cells preferentially damaged mTEC in the recipient thymus and caused defective thymic negative selection.
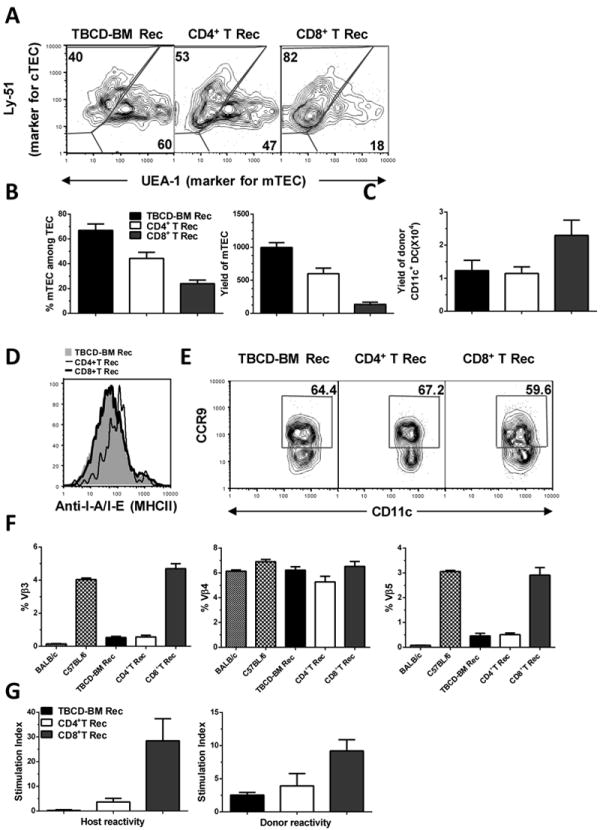
Lethally irradiated BALB/c recipients were transplanted with 0.1 ×106 CD4+ or CD8+ T cells and TBCD-BM cells from C57BL/6 donors. Recipients given TBCD-BM cells alone were used as controls. At 15 days after HCT, recipient thymus was measured for the percentage and yield of mTEC, percentage and yield of thymic CD11c+ DCs, and expression of MHC II and CCR9. At 30 days after HCT, recipient spleen cells were measured for MMTV-mediated clonal deletion of Vβ3, Vβ4, and Vβ5. In addition, flow cytometry-sorted de novo-generated donor-derived CD4+ T cells were measured for donor- and recipient-reactivity. A. Gated thymic epithelial cells are shown in UEA-1 (mTEC marker) versus Ly51 (cTEC marker). A representative flow cytometry pattern and mean ± SE of percentage and yield of mTEC is shown from1 of 4 replicate experiments. In each experiment, 6 thymi were combined from each group in order to obtain a sufficient number of thymic epithelial cells. B. Percentage and yield of mTEC, Mean ± SE, N=4. C. Total yield of donor CD11c+ DCs in the thymus, Mean ± SE, N=6. D. Expression levels of MHC II by CD11c+ DCs. E. Percentage of CCR9+CD11c+ DCs among total CD11c+ DCs. A representative flow cytometry pattern is shown from 1 of 6 samples. F. Percentage changes of Vβ3, Vβ4, and Vβ5 among de novo-generated donor-derived CD4+ T cells. Mean ± SE (N=6) is shown. G. Recipient- and donor-reactivity of de novo-generated donor CD4+ T cells. Flow cytometry-sorted, de novo-generated, donor-derived CD4+ T cells (0.2 ×106) were stimulated with donor- or recipient-type DCs (0.1×106). T cell proliferation was measured with 3H-TDR incorporation. Mean ± SE of the stimulation index from 4 replicate experiments is shown.
