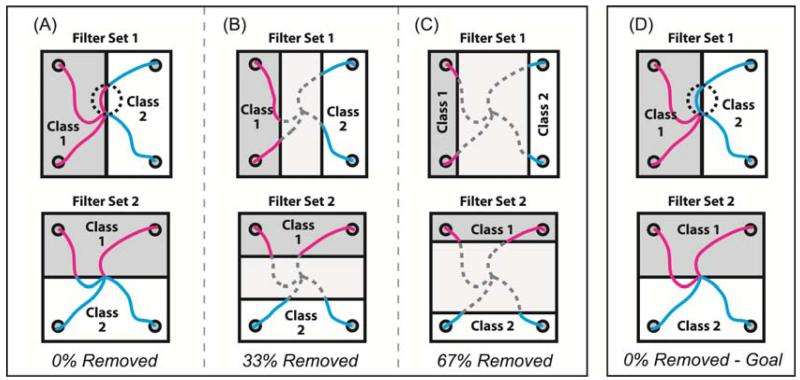
Figure 3.
Options for assigning continuous data into two classes for use with the CSP algorithm. Each square shows four example trajectories and how those data points were assigned to one of two classes based on position. Data points shown in magenta were assigned to class 1. Data points in cyan were assigned to class 2. Trajectory points shown in dashed gray lines were discarded and not used to build filters. Upper row illustrates class assignments used to build filters for extracting the horizontal component of movement, and the bottom row illustrates class assignments used to build filters for extracting the vertical component. A) All time points in a movement trajectory got assigned to one of two classes based on which half of the dividing line they were on (0% removed). B) 33% of the midrange trajectory points were discarded and only the outer 67% were assigned to each class. C) 67% of the midrange trajectory points were discarded and only the outer 33% were assigned to each class. D) All time points in a movement trajectory got assigned to their class based on which half of the workspace the intended reach goal resided.