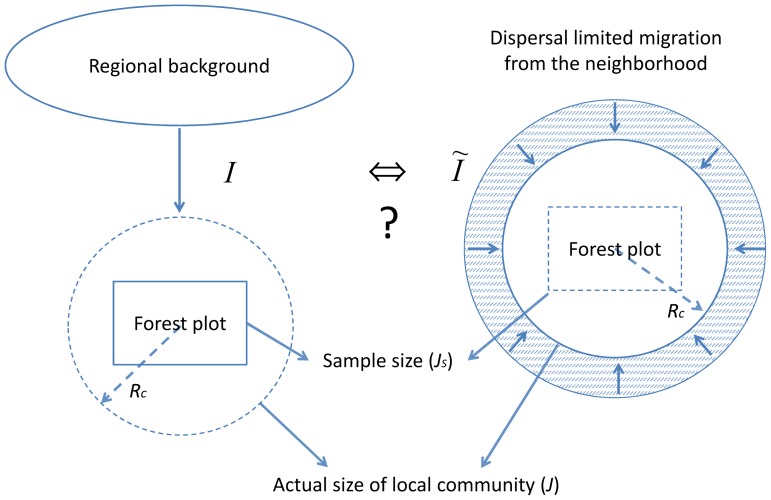
Figure 1. Comparing spatially-implicit immigration from a regional pool to a model based on seed dispersal from the community neighbourhood.
A hypothetical rectangular forest plot is shown. In a spatially-implicit framework (left), the plot is part of a discrete local community, which is related to a regional species pool via immigration. Based on the composition of the plot, the SINM based methods allow estimating the number of immigrants available for replacement of a dead individual at the scale of the entire local community. If dispersal limitation is assumed to be the only driver of immigration into the local community (right), the number of incoming individuals from the neighbourhood around the community can be modelled with the help of a dispersal kernel model.