Figure 4. CaMKII inhibition attenuates p38MAP activation and p47phox membrane translocation in rat hippocampal slice cultures exposed to oxygen glucose deprivation.
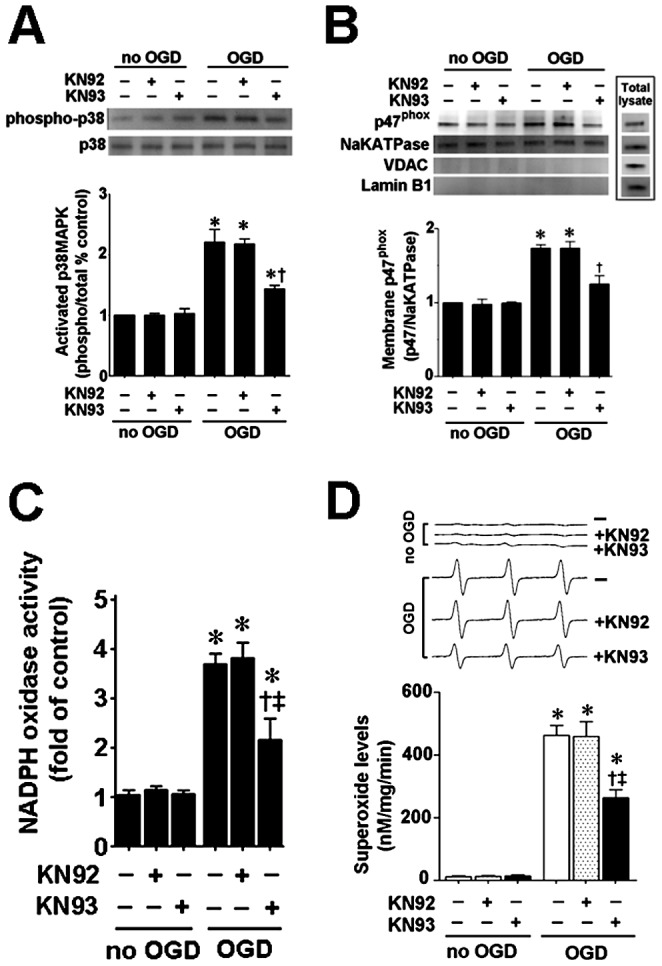
Rat hippocampal slice cultures were exposed to OGD in the presence of the CaMKII inhibitor, KN93 or its inactive analog, KN92 (10 µM, 2 h prior to OGD), harvested 2 h after OGD and subjected to Western blotting using antibodies specific to phospho- and total-p38MAPK to estimate the effect on p38MAPK activation (A). OGD increases phospho-p38MAPK to total p38MAPK ratio and this is decreased by KN93 (A). OGD increases both the plasma membrane translocation of p47phox (B) and NADPH oxidase activity (C) 2 h after OGD. KN93 pretreatment reduces both the OGD-mediated increase in p47phox membrane translocation (B) and the increase in NADPH oxidase activity (C). Slices harvested 2 h after OGD were also subjected to electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) using the spin-trap compound 1-hydroxy-3-methoxycarbonyl-2,2,5,5-tetramethylpyrrolidine HCl (CMH) to determine superoxide levels. Representative EPR waveforms are shown (D). Absolute levels of superoxide generation were determined as nmols superoxide generated/min/mg protein. KN93 pretreatment reduces the OGD-mediated increases in superoxide levels (D). Values are presented as mean ± S.E from 4 independent experiments using 24 pooled slices per experiment. * P<0.05 vs. no OGD, † P<0.05 vs. OGD alone, ‡P<0.05 vs. OGD+KN92.
