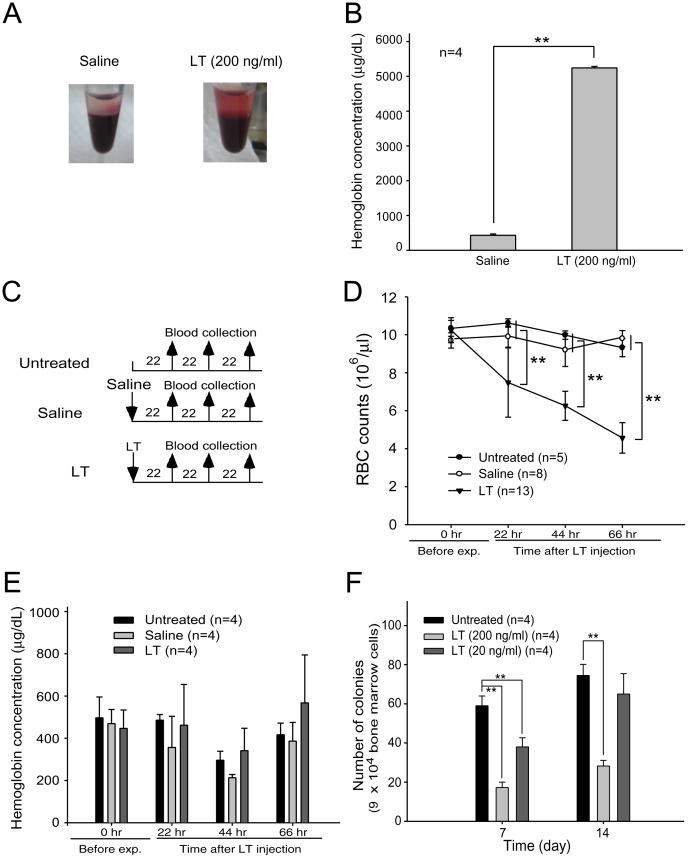
Figure 1. Effects of LT on hemolysis and in vitro erythroid colony-forming cell assay.
An image of LT (200 ng/ml)-induced hemolysis in vitro was compared with a saline-treated control group (A). After peripheral blood cells were incubated with or without LT at 37°C for 2 hours, plasma hemoglobin levels (µg/dL) were measured using Drabkin’s reagent (B). The experimental outline of the in vivo hemolysis assay is shown, in which untreated and saline-treated groups served as negative control groups (C). The RBC counts (D) and the levels of cell-free plasma hemoglobin (E) were determined 22, 44, and 66 hours after the mice were treated with LT. The in vitro erythroid colony-forming cell assay was performed by incubating murine BM cells with or without LT (200 ng/ml or 20 ng/ml). Colonies of progenitor cells were counted on Days 7 and 14 post-erythroid differentiation initiation (F). Untreated BM cells were used as a control. ** p<0.01, comparisons between groups are indicated. Data are reported as mean ± SD.