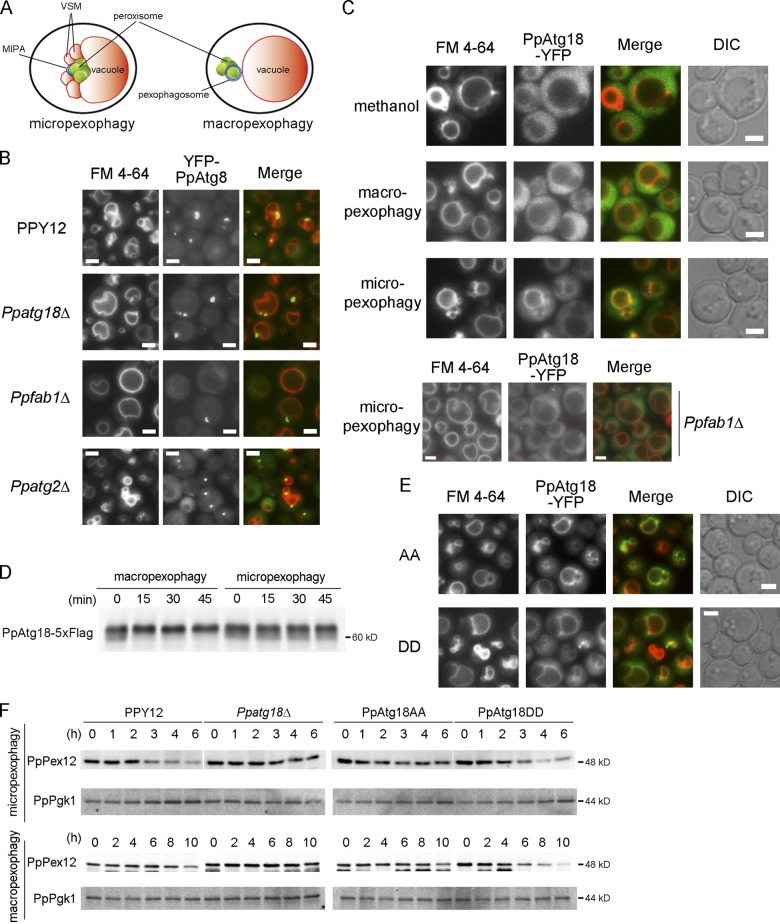
Figure 6.
Phosphorylation of PpAtg18 regulates VSM formation in micropexophagy. (A) Intracellular structures observed during micropexophagy and macropexophagy. MIPA, micropexophagy-specific membrane apparatus; VSM, vacuolar sequestering membrane. (B) Fluorescence microscopy analysis during micropexophagy. Cells were shifted from methanol medium to glucose medium for 30–60 min to induce micropexophagy. Vacuoles were stained with FM 4-64, and MIPA was visualized by YFP-tagged PpAtg8 expressed under the PpATG8 promoter. (C) Intracellular localization of PpAtg18. YFP C-terminally tagged with PpAtg18 was expressed in Ppatg18Δ under the PpATG18 promoter. Cells were shifted from methanol medium to ethanol or glucose medium for 30–60 min to induce macropexophagy or micropexophagy, respectively. (D) Immunoblot detection of PpAtg18-5×Flag. PpAtg18-5×Flag was expressed in Ppatg18Δ under the PpATG18 promoter. Cells were shifted from methanol medium to ethanol or glucose medium to induce macropexophagy or micropexophagy, respectively. This blot was incubated with the anti-FLAG antibody. (E) Intracellular localization of PpAtg18 AA and DD during micropexophagy. YFP-tagged PpAtg18 mutants were expressed under the PpATG18 promoter. Cells were shifted from methanol medium to glucose medium for 60 min to induce micropexophagy. Bars, 2 µm. (F) PpPex12 degradation assay to assess micropexophagy and macropexophagy activity in PpAtg18 mutants. Strains were grown in methanol medium and then shifted to glucose or ethanol medium to induce micropexophagy or macropexophagy, respectively. Cell-free extracts were prepared and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-PpPex12 or anti-Pgk1 antibodies. Optical density measurements showed no significant difference in growth between these mutants.