FIG 4 .
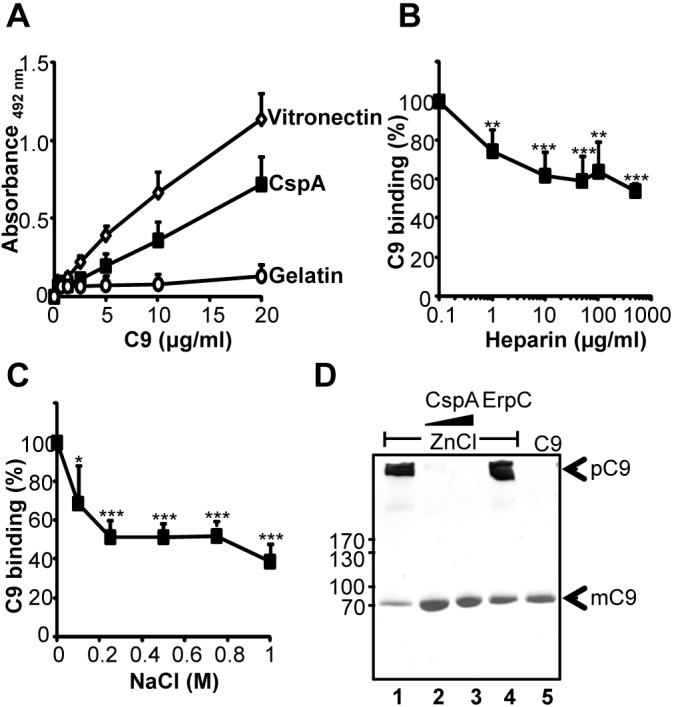
CspA binds to C9 and inhibits C9 polymerization. (A) C9 binds to immobilized CspA, and the effect is dose dependent. Binding of C9 (0.01 to 20 µg/ml) to immobilized CspA (5 µg/ml) was assayed by ELISA, and bound C9 was detected with polyclonal C9 antiserum followed by HRP-conjugated anti-goat antibody. (B) Heparin affects the CspA-C9 interaction. The effect of heparin (1 to 500 µg/ml) on binding of C9 (5 µg/ml) to immobilized CspA (5 µg/ml) was assayed. (C) NaCl inhibits the CspA-C9 interaction. The effect of NaCl (0.1 to 1 M) on binding of C9 (5 µg/ml) to immobilized CspA (5 µg/ml) was assayed. The mean values from three separate experiments are shown, and error bars show SD. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001. (D) CspA inhibits polymerization of C9. ZnCl2 induced C9 polymerization, and after incubation the samples were separated by SDS-PAGE. Following silver staining, C9 polymers and C9 monomers were identified by their mobility. C9 polymerizes in the presence of ZnCl2 (lane 1). CspA (2.5 and 5 µg) blocks polymer formation (lanes 2 and 3). The borrelial immune evasion protein ErpC (5 µg) (lane 4) does not influence C9 polymerization. In the absence of ZnCl2, C9 does not form polymers (lane 5). The data shown are representative of three independent experiments.
