Figure 2. Effect of SR4 on cell cycle progression in melanoma.
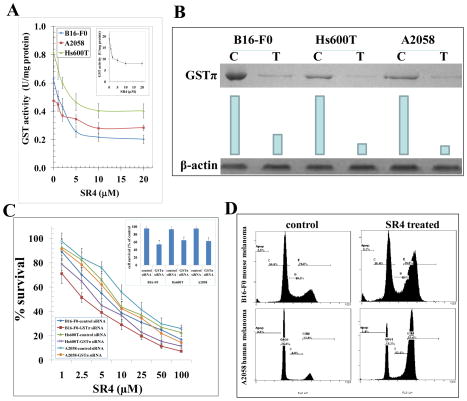
GST activity towards 1-chloro 2,4-dinitro benzene (CDNB) and its inhibition by SR4 was performed in 28000g crude supernatant prepared from B16-F0, Hs600T and A2058 cells. Human liver purified GST was used as a control (inset). The inhibitory effect of SR4 on GST was studied at a fixed concentration of GSH and CDNB (1 mM each) and varying concentrations of inhibitor. The enzymes were pre-incubated with the inhibitor for 5 min at 37 °C prior to the addition of the substrates (panel A). Depletion of GSTπ by siRNA and its effects on cell survival by MTT assay: GSTπ siRNA or a scrambled control was transfected into melanoma cell lines using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen). After knock-down of GSTπ by siRNA, the level of GSTπ was detected by Western blot analyses. Membranes were stripped and reprobed for β-actin as a loading control. Results were quantified by scanning densitometry: C, control siRNA; T, GSTπ siRNA (panel B). MTT assay in GSTπ siRNA transfected cells were performed 96 h after SR4 treatment. The values are presented as mean ± SD from two separate determinations with eight replicates each (n = 16) (panel C). GSTπ-depletion itself caused decreased in cell growth( panel C inset), * p<0.01 compared to control. Inhibitory effect of SR4 on cell cycle distribution was determined by fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis (panel D). The experiment was repeated three times and similar results were obtained.