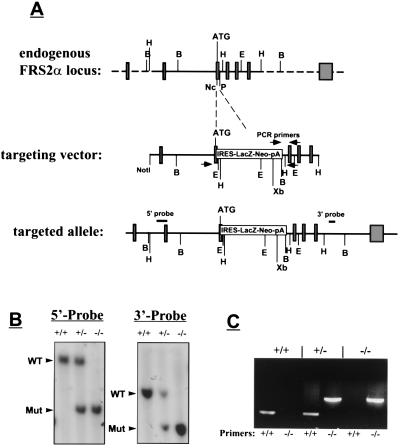
Figure 1.
Targeted disruption of the Frs2α locus. (A) Strategy for generation of Frs2α mutation. The targeting vector contains a β-galactosidase neomycin resistance cassette in place of a 0.5-kb region of Frs2α gene that includes the first coding exon. Open boxes mark noncoding exons, and shaded boxes mark coding regions. Arrowheads mark the primers for genotyping by PCR, and the locations of the internal 5′ and external 3′ probes that were used for Southern blotting are also indicated. Restriction sites for several restriction enzymes are indicated. B, BamHI; E, EcoRI; H, HindIII; Nc, NcoI; P, PstI; Xb, XbaI. (B) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA isolated from ES cell lines. For hybridization with the 5′ internal probe, DNA was digested with XbaI; for hybridization with the 3′ external probe, DNA was digested with BamHI. Arrows mark the positions of wild-type or mutant fragments. The sizes of these fragments are: 5′ probe: wild type 12 kb, mutant 7 kb; 3′ probe: wild type 8 kb, mutant 5 kb. (C) PCR analysis of Frs2α mutation. DNA was isolated from ES cell lines and PCR was performed as described in Methods. Two sets of primers were used, one for the wild-type allele (+/+) and the other for the Frs2α mutant allele (−/−).