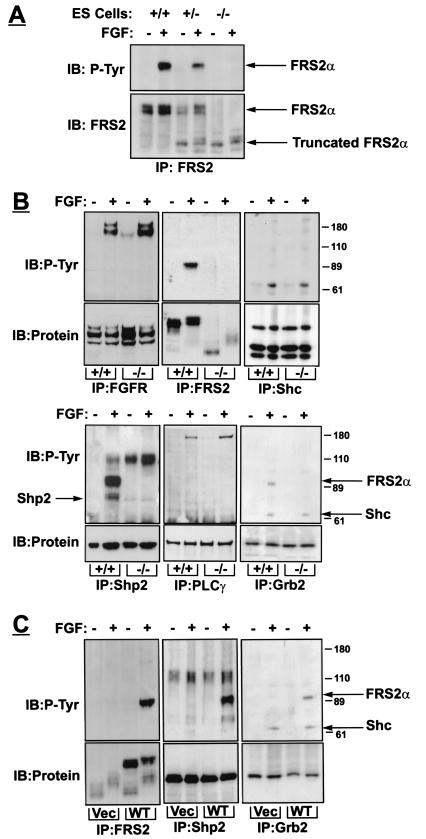
Figure 2.
Biochemical characterization of FRS2α-deficient fibroblasts. (A) Expression and tyrosine phosphorylation of FRS2α in wild-type, heterozygous, and homozygous FRS2α mutant cells. ES cells grown on gelatin in the presence of 1 μM retinoic acid for 24 h, starved overnight, treated with FGF1 (100 ng/ml) and heparin (5 μg/ml) for 5 min, lysed, and subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-FRS2 antibodies followed by immunoblotting with anti-FRS2 or anti-pTyr antibodies. (B) Mouse embryo fibroblasts were serum-starved overnight, treated with FGF1 (100 ng/ml) and heparin (5 μg/ml) for 5 min, lysed, and immunoprecipitated with antibodies as indicated. (C) FRS2α mutant fibroblasts were infected with retroviral expression vector for wild-type FRS2α or with vector alone. Fibroblasts were treated with FGF1, and cell lysates were immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted with different antibodies as indicated.