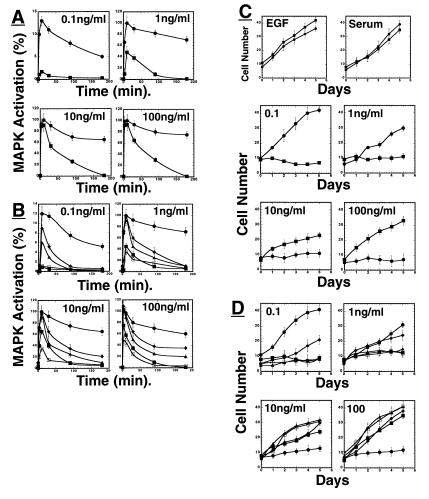
Figure 4.
Impaired FGF-induced MAP kinase (ERK) stimulation and cell proliferation of FRS2α-deficient fibroblasts. (A) Comparison of MAP kinase activation in wild-type or FRS2α-deficient fibroblasts in response to FGF1 stimulation. Fibroblasts were starved, treated with different concentrations of FGF1, lysed, and immunoblotted with phospho-specific MAP kinase antibodies or with anti-Erk1 antibodies, and the intensity of the protein bands was quantitated by densitometry. ●, Wild-type fibroblasts; ■, FRS2α-deficient fibroblasts. (B) FRS2α mutant fibroblasts were infected with expression vector encoding for wild-type FRS2α or mutant FRS2α, or with vector alone. MAP kinase stimulation was revealed by immunoblotting with anti-phospho-MAP-kinase antibodies followed by quantitation by densitometry. ●, Wild-type FRS2α; ▴, ♦, or □, the 2F, 4F, or 6F FRS2α mutants; ■, vector alone. Similar results were obtained in three different experiments. (C) Growth curves of wild-type and FRS2α-deficient fibroblasts in response to growth factor stimulation. Wild-type or FRS2α mutant fibroblasts were grown in medium containing 10 ng/ml EGF, 10% serum, or different concentrations of FGF. The cells were trypsinized at the indicated time points and counted. ● Wild-type fibroblasts; ■ FRS2α-deficient fibroblasts. (D) FRS2α-deficient fibroblasts were infected with expression vector for wild-type FRS2α, FRS2α mutants, or vector alone. The cell lines were stimulated with different concentrations of FGF and growth curves were determined. ●, Wild-type FRS2α; ▴, ♦, or □, the 2F, 4F, or 6F FRS2α mutants; ■, vector alone.