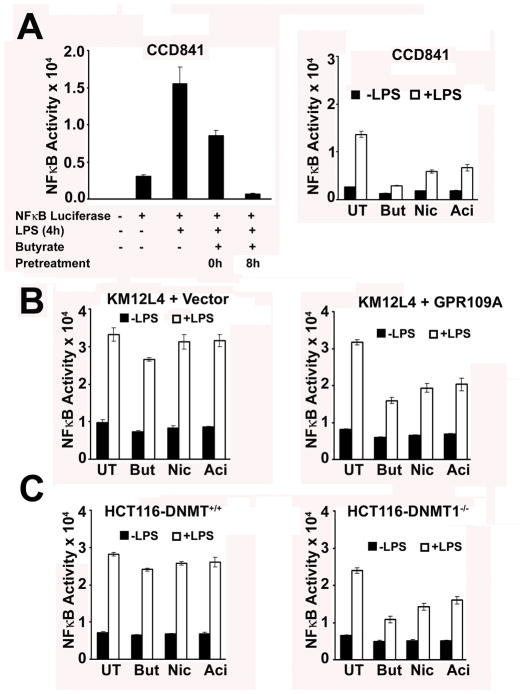
Figure 5.
Blockade of LPS-induced NF-κB activation by GPR109A in the normal colon cell line CCD841 and in the colon cancer cell lines KM12L4 and HCT116. A, CCD841 cells were first transfected with a NF-κB-luciferase reporter construct. 24h later, cells were treated with LPS (100 ng/mL) for 4h with or without pretreatment with butyrate (But, 1 mM), nicotinate (Nic, 1 mM), or acifran (Aci, 0.25 mM) for 4h. The ligands were present for an additional 4h during treatment with LPS. LPS-induced activation of NF-κB was monitored by measuring the activity of luciferase as a reporter. UT, no treatment with GPR109A ligands. B, KM12L4 cells were transfected with a NF-κB-luciferase reporter together with either vector or GPR109A cDNA. 24h later, cells were treated with LPS (100 ng/mL) for 4h with or without pretreatment with butyrate (But, mM), nicotinate (Nic, 1 mM), and acifran (Aci, 0.25 mM) for 4h. In addition to the pretreatment, the ligands were present also during LPS treatment. LPS-induced activation of NF-κB was monitored by measuring the activity of luciferase as a reporter. C, HCT116 cells (DNMT+/+ and DNMT1−/−) were transfected with a NF-κB-luciferase reporter construct. 24h later, cells were treated with LPS (100 ng/mL) for 4h with or without pretreatment with butyrate (1 mM), nicotinate (1 mM), or acifran (0.25 mM) for 4h. The ligands were present also during LPS treatment. LPS-induced activation of NF-κB was monitored by measuring the activity of luciferase. UT, no treatment with GPR109A ligands.