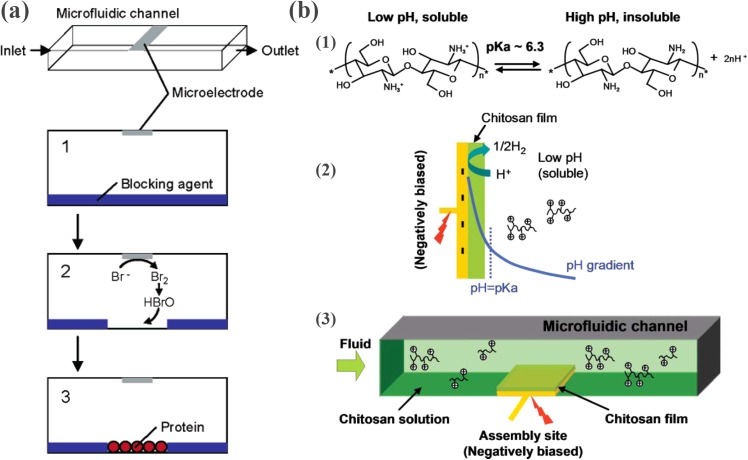
Figure 22.
(a) Electrochemically activated protein immobilization within a sealed microchannel. (1) Introduce a blocking agent (polyethyleneimine (PEI) and heparin) through the microchannel for antibiofouling, (2) generate HBrO local to the microelectrode, which removes a portion of blocking agent, thus making this part of the channel bottom available to protein physisorption, and (3) introduce proteins into the microchannel for immobilization. Reprinted with permission from H. Kaji et al., Anal. Chem. 78, 5469 (2006). Copyright 2006 American Chemical Society. (b) Chitosan-based electrochemically activated protein immobilization on gold electrode. (1) pH dependent protonation/deprotonation of the chitosan molecule, (2) schematic view of chitosan deposition, and (3) schematic view of chitosan deposition in a microfluidic channel. Reprinted with permission from J. J. Park et al., Lab Chip 6, 1315 (2006). Copyright 2006 The Royal Society of Chemistry.