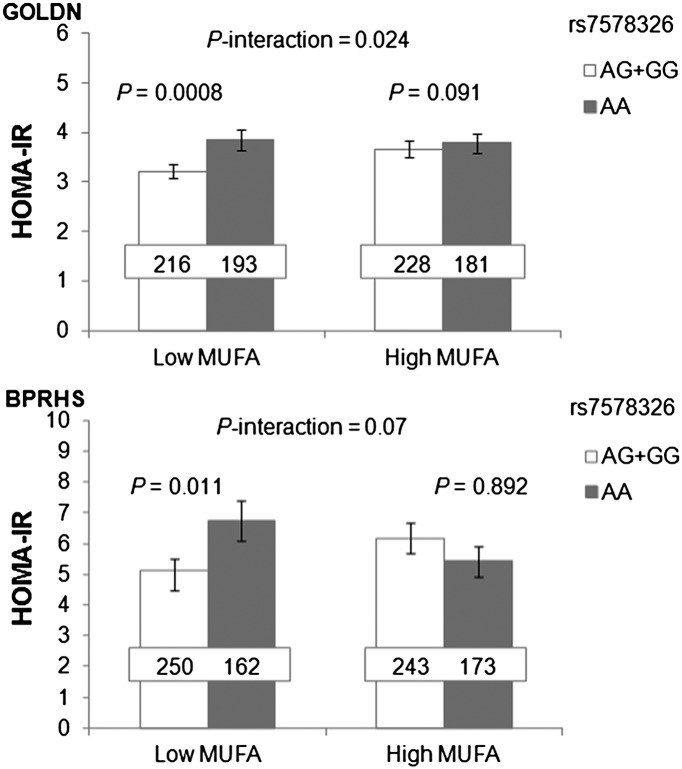
Figure 1.
Interaction of IRS1 variant with dietary MUFA on insulin resistance in the GOLDN and BPRHS populations. Dietary MUFA interacted significantly (P = 0.024) with IRS1 variant rs7578326 on insulin resistance in GOLDN and marginally significantly (P = 0.07) in BPRHS. In both populations, G-allele carriers of rs7578326 had significantly lower HOMA-IR than noncarriers only when dietary MUFA intake was low (≤median intake of each population), but not when MUFA intake was high. P values in GOLDN were adjusted for age, sex, waist circumference, study center, smoking status, alcohol drinking, type 2 diabetes, physical activity, and family relationships. P values in the BPRHS were adjusted for age, sex, waist circumference, smoking status, alcohol drinking, type 2 diabetes, physical activity, and population structure. Number inside the bar indicates the number of subjects in that group. Values are means ± SEM.