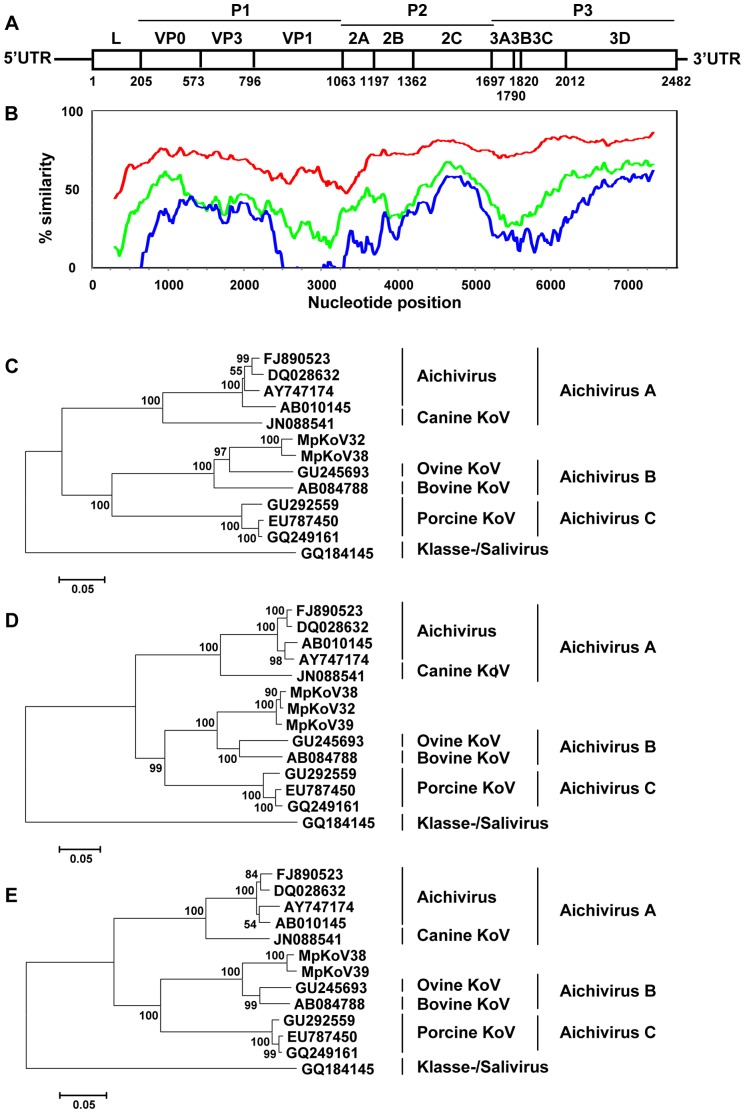
Figure 2. Genome organization of ferret kobuvirus and amino acid sequence divergence from other aichiviruses.
(A) Predicted genome organization of ferret kobuvirus showing amino acid positions of predicted cleavage sites in the polyprotein (numbering based on the ferret kobuvirus polyprotein sequence). Sites were predicted by NetPicoRNA analysis and by alignment with known cleavage sites in aichiviruses. (B) Mean similarity of bovine kobuvirus (AB084788) to ferret kobuvirus (red), porcine kobuvirus (GU292559, green), and human aichivirus (FJ890523; blue) polyprotein-coding nucleotide sequences scaled to the genome diagram in A. (C–E) Phylogenetic trees of the amino acid sequences of ferret kobuvirus (MpKoV32, 38, and 39) with other aichiviruses in the P1 (C), P2 (D), and P3 (E) gene regions were generated using MEGA5, with the neighbor-joining method with p-distance and 1,000 bootstrap replicates. Significant bootstrap values are shown.