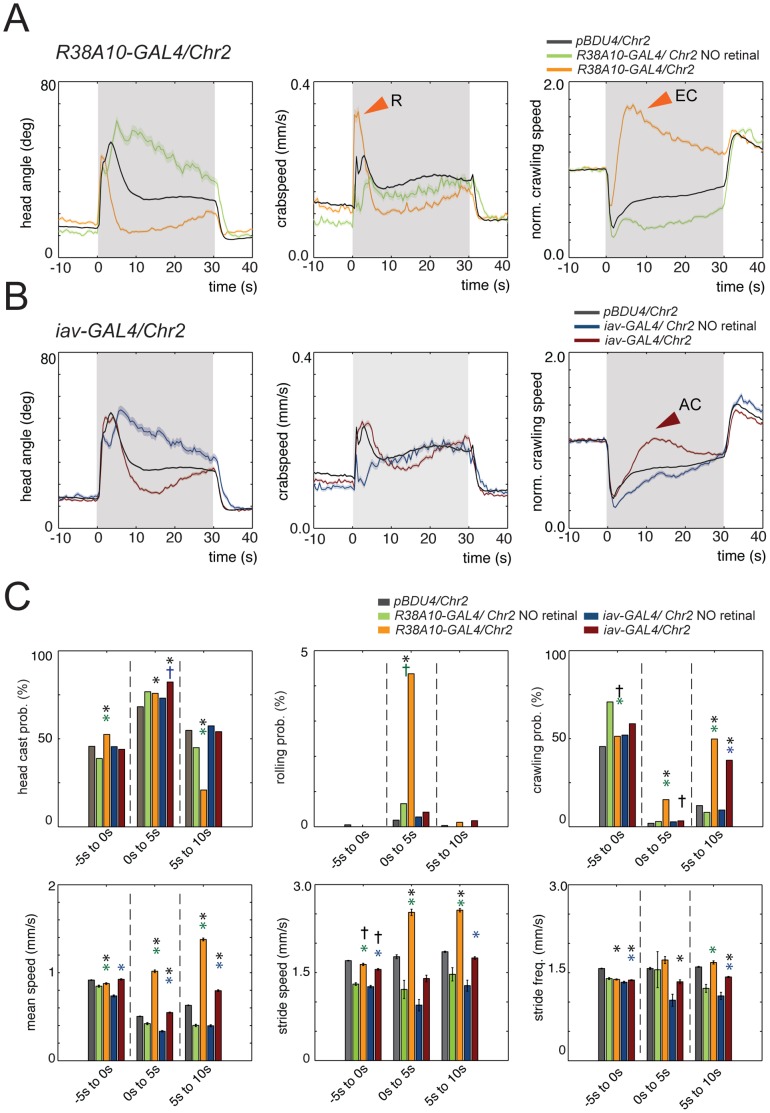
Figure 9. Larval reactions to optogenetic ChR2 activation of sensory neurons.
(A and B) Graphs show head angle, and crabspeed and norm. crawling speed, as a function of time averaged across many animals from experiments in which larvae were presented with 30 s of continuous 470 nm light, at 25°C. Gray shading indicates the period of stimulation. Dark lines, mean value. Light lines, ± s.e.m. R, roll. EC, escape crawl. AC, avoidance crawl. Larvae with activated class IV (R38A10>ChR2, orange, N = 806) or ch (iav>ChR2, red, N = 1213) neurons are compared to no-retinal (R38A10>ChR2 no-retinal, green, N = 305 and iav>ChR2 no-retinal, blue, N = 361) and no-GAL4 controls (pBDPGAL4U>ChR2, black, N = 23305). Activation of class IV neurons evokes a peak in the crabspeed function (corresponding to the roll, R), followed by an increase in norm. crawling speed (corresponding to escape crawl, EC) compared to controls. Activation of ch neurons evokes a clear increase in norm. crawling speed during stimulation, resembling the avoidance crawl (AC) observed during vibration stimulation. Note also an increase in norm. crawling speed in response to 470 nm light offset in all tested lines (the off-reaction to light). (C) Bar charts show head casting, rolling and crawling probability and the absolute larval crawling speed, the maximum stride speed and stride frequency in a 5 s time window before stimulation (−5 s to 0 s) and in two consecutive 5 s time windows after stimulation (0 s to 5 s and 5 s to 10 s). Error bars indicate s.e.m. * or *, p<0.001.+or +, p<0.01. green, blue and black, indicate comparison to R38A10>ChR2-no-retinal, iav>ChR2-no-retinal and pBDPGAL4U>ChR2 controls, respectively. Activation of class IV neurons evokes a mild, but significant increase in rolling probability (4.3%) relative to both controls (0.6%, N = 305, p = 0.004468 and 0.2%, N = 23305, p<10−6 for no-retinal and no-GAL4, respectively) and a significant increase in crawling probability, mean absolute crawling speed and mean stride speed and a mild but significant increase in stride frequency (see Table S4 for details). Activation of ch neurons evokes a significant increase in head cast probability immediately following stimulation (82.3%, N = 1213) compared to both controls (73.1%, N = 361, p = 0.001584 and 68.2%, N = 23305, p<10−6 for non-retinal and no-GAL4, respectively) and a significant increase in crawling probability and mean absolute crawling speed relative to both controls (see Table S4 for further details).