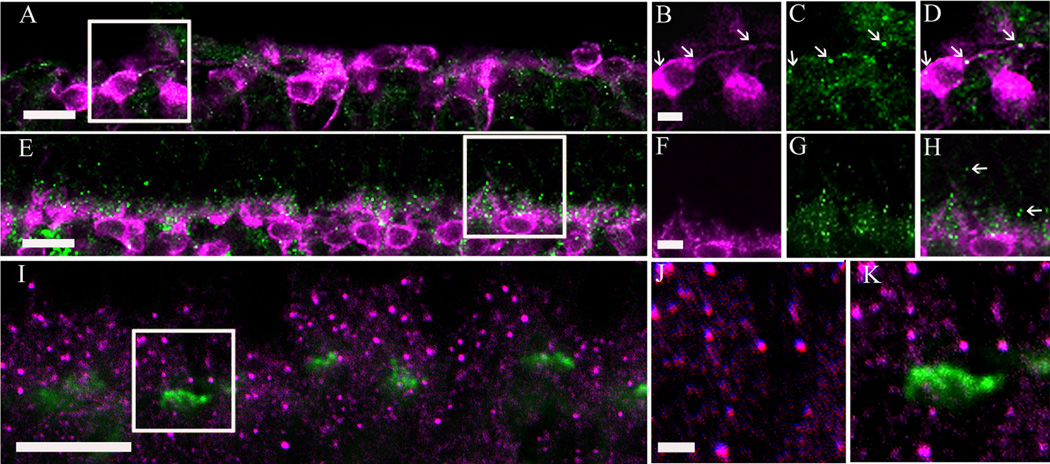
Figure 8.
α2δ4 subunit immunoreactivity was observed in photoreceptor terminals of the mouse retina. A: α2δ4 subunit and protein kinase C (PKC) immunoreactivity in a rd/rd adult mouse retina that lacks photoreceptors (Carter-Dawson et al., 1978). B–D: High-magnification view of a single scan (boxed area from A). α2δ4 subunit immunoreactivity was significantly reduced in the rd/rd adult mouse OPL and some of the remaining α2δ4 subunit immunoreactive puncta (green) colocalized with rod bipolar cell terminals (arrows) immunostained with PKC antibodies (magenta). E: α2δ4 subunit and PKC immunoreactivity in cone-DTA mice. These mice lack cone photoreceptors (Soucy et al., 1998). F–H: High-magnification view of single scan (boxed area from E) showing α2δ4 subunit immunoreactive puncta distal to rod bipolar cell dendrites (arrows) suggesting the presence of the α2δ4 subunit at rod photoreceptor terminals. I: Labeling of cone pedicles with peanut agglutinin (PNA) conjugated to FITC (green) and α2δ4 subunit antibody (magenta) in the wild-type mouse. J,K: High-magnification view of single scan showing that α2δ4 subunit immunoreactivity is not located at the base of cone pedicles. Scale bar = 10 µm in A,E,I; 2 µm in B (applies to B–D), F (applies to F–H), and J (applies to J,K).