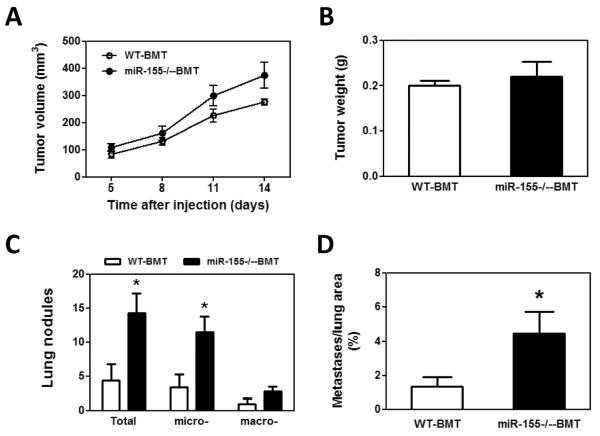
Figure 1.
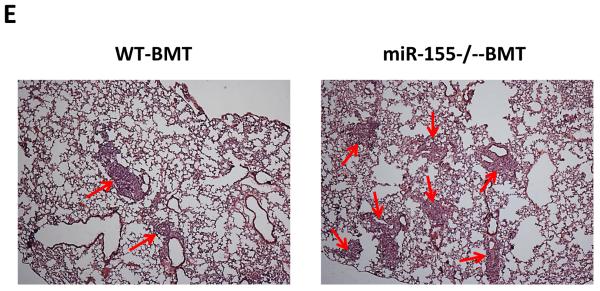
Enhanced lung metastasis in miR-155−/− chimeric mice. A, Growth rate of LLC primary tumors in WT and miR-155−/− chimeric mice. 1×107 LLC cells were subcutaneously implanted in the back of WT and miR-155−/− chimeric mice and tumor size was measured with a caliper. Tumor volume was shown as mm3. B, Average tumor weight at day 14 after LLC inoculation. C, Quantification of average number of nodules in lung of WT and miR-155−/− chimeric mice on 14 days post LLC cell implantation. Nodules smaller than 70 μm are defined as micro-metastases (micro-). Nodules larger than 70 μm are defined as macro-metastases (macro-). D, The percentage of metastatic area in lung tissues was calculated (n=8 mice per group). E, Representative H&E staining sections of the lungs from WT and miR-155−/− chimeric mice (n=8) carrying LLC tumors. The red arrows point to the metastatic nodules in the lungs. Magnification, × 4. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of 8 mice. *p<0.05 by Student's t test.