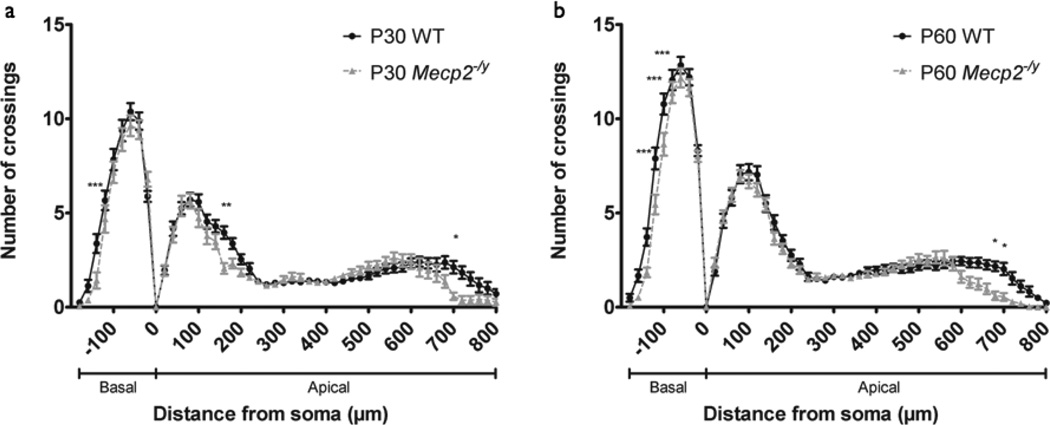
Figure 2. Dendritic complexity in somatosensory cortex of Mecp2−/ymice.
(a) Sholl analysis of somatosensory cortex layer V pyramidal neurons in P30 WT (n=24 neurons from 4 mice) and Mecp2−/y mice (n=19 neurons from 4 mice) shows reduced dendritic complexity in Mecp2−/y mice relative to WT. Basal dendritic arbor is denoted b negative distance from soma, 0 urn marks soma position within cortex, and apical dendritic arbor is denoted by positive distance from soma. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction, p<0.0001 (interaction); *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. Bars represent mean ± sem.
(b) Sholl analysis of somatosensory cortex layer V pyramidal neurons in P60 WT (n=36 neurons from 4 mice) and Mecp2−/y mice (n=31 neurons from 4 mice) show more widespread reduction in dendritic complexity in Mecp2−/y mice relative to WT than seen in P30 animals. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction, p<0.0001 (interaction); *p<0.05, ***p<0.001.