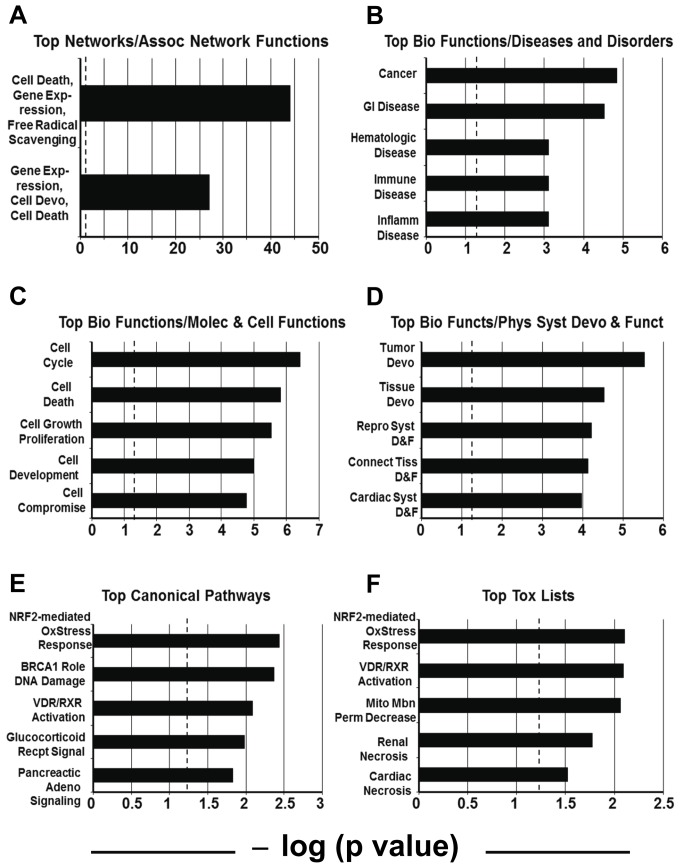
Figure 6. Integrated Pathway Core Analysis of the 30 upregulated polysome-fraction mRNAs (DTT-treated U87 cells vs untreated).
Using Integrated Pathway Analysis algorithms, the identified messages were grouped into networks of associated functions, disease and toxicology relationships, and molecular, cellular, developmental, and physiological functions and pathways. Each grouping shows the top two or top five highest scoring categories (based on statistical significance from a Fisher Exact Test, significance set at p<0.05). X axes show this as a –log (p value), with hatched lines at 1.25 as the threshold for significance. Of the Top Networks, (A) shows the only significant Associated Network Functions identified for the 30 gene product set, “Cell Death, Gene Expression, Free Radical Scavenging” and “Gene Expression, Cellular Development, Cell Death”. (B, C, D) show the Top Biologic Functions with the following subheadings: In Diseases and Disorders (B), the top 5 categories were Cancer, Gastrointestinal Disease, Hematological Disease, Immunological Disease, and Inflammatory Disease. In Molecular and Cellular Functions (C), the top 5 categories are Cell Cycle, Cell Death, Cellular Growth and Proliferation, Cellular Development, and Cellular Compromise. In Physiological System Development and Function (D), the top 5 categories were Tumor Development, Tissue Development, Reproductive System Development and Function (“D & F”), Connective Tissue Development and Function, and Cardiovascular System Development and Function. There were 72 significantly scoring Biologic Functions overall (data not shown). (E) shows the top 5 (of 9 total) significantly scoring Canonical Pathways, including NRF-2 (Nuclear factor [erythroid-derived 2]-like 2)-mediated Oxidative Stress Response, Role of BRCA1 in DNA Damage Response, Vitamin D Receptor/Retinoic Acid X Receptor Activation, Glucocorticoid Receptor Signaling, and Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Signaling. The Top Toxicology Lists (F) include NRF-2 (Nuclear factor [erythroid-derived 2]-like 2)-mediated Oxidative Stress Response, Vitamin D Receptor/Retinoic Acid X Receptor Activation, Decreased Permeability Transition of Mitochondria and Mitochondrial Membrane, Renal Necrosis/Cell Death, and Cardiac Necrosis/Cell Death.