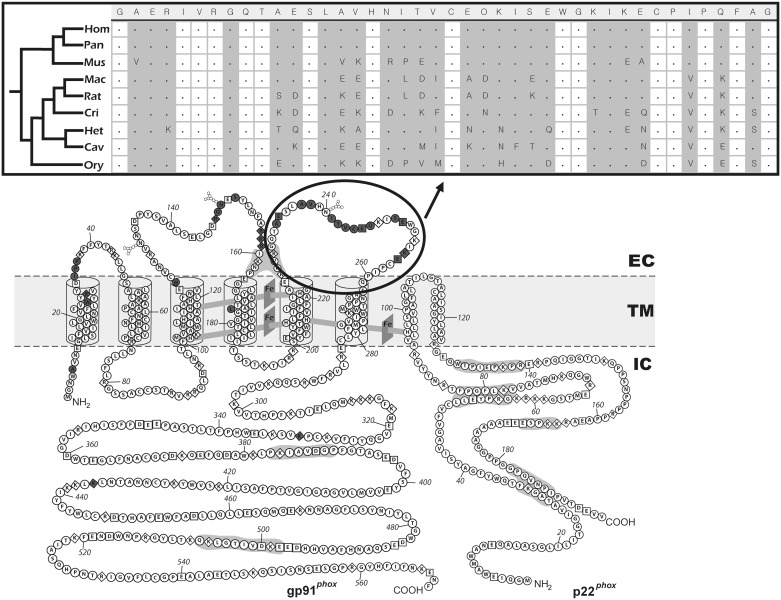
Fig. 3.
Natural selection mapping across CYBB (encoding gp91) along mammalian evolution, as identified using the PAML method by Yang (2007a). The topologies of gp91 and p22 are reproduced from Taylor et al. (2004, Copyright 2004. The American Association of Immunologists, Inc. Used with permission.). Dark gray amino acids have evolved under positive selection with >80% probability. Most of these amino acids are in the extracellular portion of the protein. The upper part of the figure shows the protein alignment for nine mammals of the gp91 region indicated by the black ellipse. In this region, a high level of amino acid variation is found between species, and several codons show ω > 1. In this alignment, gray vertical bars correspond to variable amino acid sites. The protein alignment of mammals shows the following species: Hom (Homo sapiens sapiens), Pan (Pan troglodytes), Mac (Macaca mulatta), Mus (Mus musculus), Rat (Rattus norvegicus), Cri (Cricetulus griseus), Het (Heterocephalus glaber), Cav (Cavia porcellus), and Ory (Oryctolagus cuniculus). EC, extracelular environment; TM, transmembrane layer; and IC, intracellular environment.