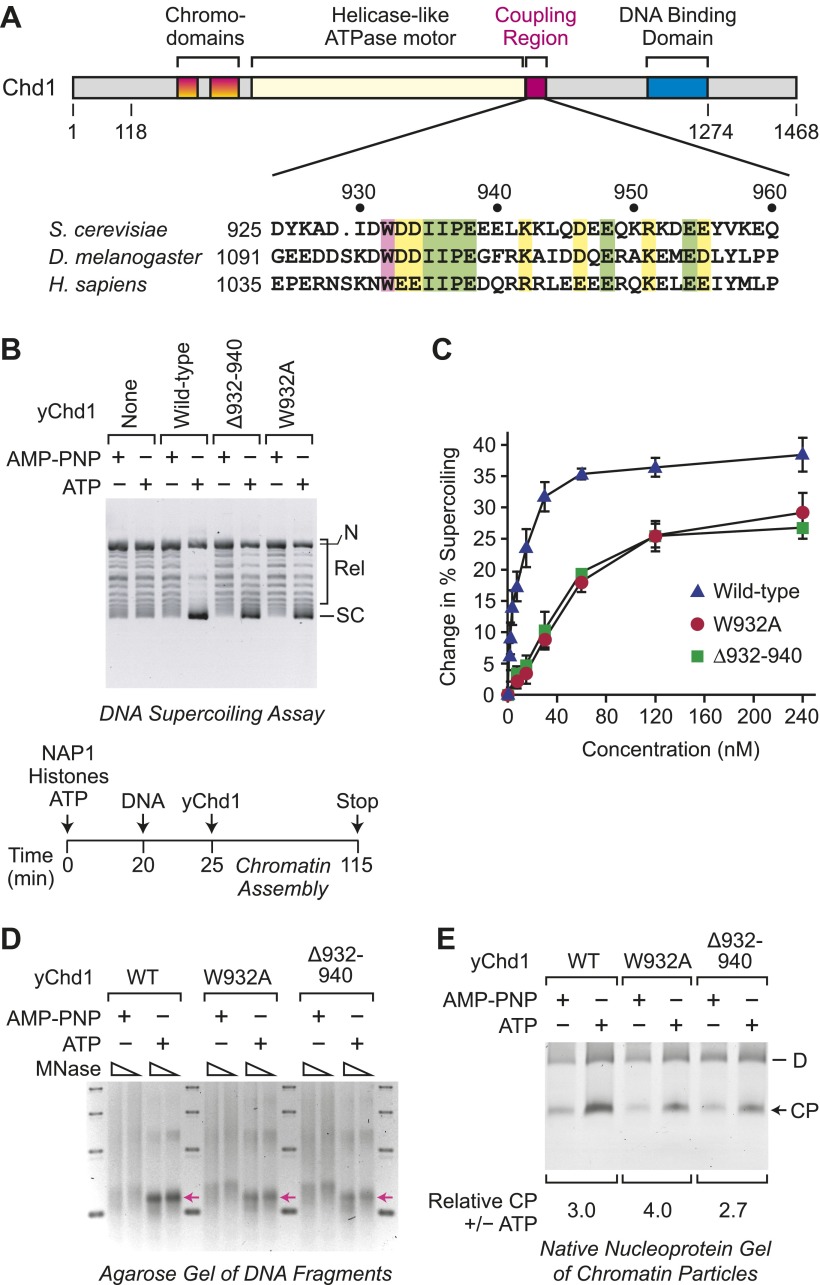
Figure 1. ATP-dependent nucleosome assembly is functionally distinct from chromatin remodeling.
(A) Diagram of Chd1 and the conserved coupling region. The numbers below the schematic diagram and above the amino acid sequences indicate positions in S. cerevisiae Chd1 (yChd1). (B) Chromatin remodeling-defective mutant yChd1 proteins (yChd1Δ932–940; yChd1W932A) can assemble nucleosomes in an ATP-dependent manner. Chromatin assembly reactions were performed with wild-type or mutant yChd1 proteins (120 nM) in the presence of either adenylyl-imidodiphosphate (AMP-PNP) or ATP. The efficiency of nucleosome assembly was monitored by the DNA supercoiling assay. The positions of supercoiled (SC), relaxed (Rel), and nicked open circular (N) DNAs are indicated. (C) Quantitative analysis of the efficiency of nucleosome assembly by mutant vs wild-type yChd1 proteins. Chromatin assembly reactions with yChd1 proteins were analyzed by the DNA supercoiling assay. The change in % supercoiling ([Δ supercoiled DNA/total DNA) × 100%) vs concentration of yChd1 (nM) is shown. The results are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (N ≥ 3). (D) Agarose gel electrophoresis of DNA fragments derived from chromatin assembled with wild-type or mutant yChd1 proteins. Chromatin assembly reactions were carried out as in (B), except that the concentration of Chd1 proteins was 60 nM. The reaction products were digested extensively with micrococcal nuclease (MNase) and subsequently deproteinized. The resulting DNA fragments were resolved on a 3% agarose gel and visualized by staining with ethidium bromide. The arrows indicate the position of DNA fragments derived from core particles. (E) Native nucleoprotein gel analysis of nucleosomes assembled with wild-type or mutant yChd1 proteins. Chromatin assembly reactions were carried out as in (D). The reaction products were digested extensively with MNase; the resulting nucleoprotein complexes were subjected to electrophoresis on a nondenaturing 5% polyacrylamide gel; and the DNA was stained with Sybr Green I (Invitrogen). The positions of core particles (CP) and dinucleosomes (D) are indicated.