Fig. 1.
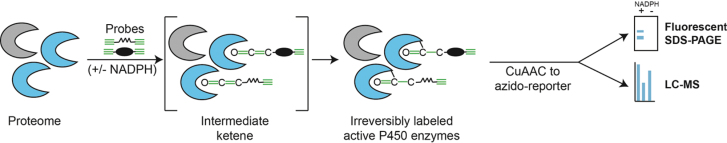
A proteome sample containing active cytochrome P450 enzymes is treated with two chemical probes developed from known mechanism-based inhibitors of P450s. Each probe contains an alkyne for reaction with the catalytic machinery of the enzyme and a second alkyne for CuAAC. In the presence of NADPH, reactive P450s oxidize a probe alkyne to a reactive ketene, which in turn acts as an electrophile and irreversibly reacts with a nucleophilic moiety within the P450 active site. Using CuAAC, reporter groups can be appended for downstream measurement of probe-labeled proteins, for example, an azido-tetramethylrhodamine for fluorescent imaging, or an azido-biotin for subsequent streptavidin-mediated enrichment and LC-MS analysis.
