Figure 1.
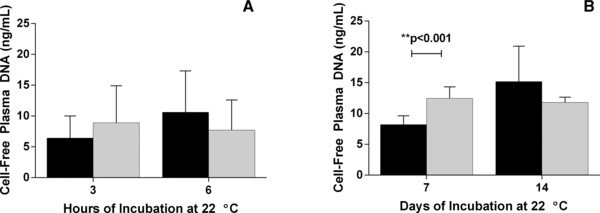
Effect of the novel chemical cocktail on plasma DNA (pDNA) detection by qPCR. Blood was drawn into K3EDTA tubes and plasma was separated by centrifugation. The plasma supernatant was aliquoted and divided into two treatment groups. To one group of plasma samples (gray bars), the chemical cocktail from a BCT was added at a final concentration equal to the amount present in a standard 10 ml blood drawn. The other group of plasma samples (black bars) was untreated and served as a control. Samples from each group were processed at 3 and 6 hr (panel A) and at 7 and 14 days (panel B). The pDNA concentration was determined using the β‐actin qPCR assay. When compared to untreated samples, samples treated with the chemicals showed no decrease in either DNA extraction from plasma or its amplification by qPCR. Error bars indicate SD, n = 5 for both panels.
