Figure 1. SFB colonization of host gut-commensal flora enhances the severity of autoimmune disease in a T cell transfer model of arthritis.
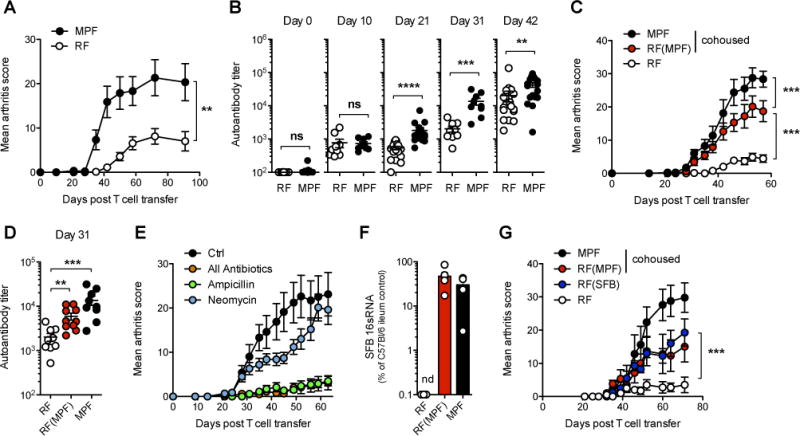
(A) Weekly arthritis score and (B) serum autoantibody titers in RF- or MPF-housed mPCC, Cd3e−/− hosts at indicated time points after naïve 5C.C7 T cell transfer. Data (mean±SEM) pooled from two (A) and four (B) independent experiments (n=9 and 18 mice per group respectively).
(C–D) One group of RF-housed mPCC, Cd3e−/− mice was cohoused with MPF-housed hosts for 3 weeks prior to T cell transfer (RF(MPF)). (C) Bi-weekly arthritis scores and (D) autoantibody titers at day 31. Data (mean±SEM) pooled from two independent experiments (n=9 RF, n=10 RF(MPF) and n=8 MPF).
(E) Various antibiotic formulations were given in the drinking water of MPF-housed mPCC, Cd3e−/− mice starting 3 weeks prior to T cell transfer and maintained for the length of the experiment. “All antibiotics” formulation contains ampicillin, neomycin, vancomycin and metronidazole. Data (mean±SEM) pooled from two independent experiments (n=10 mice per group).
(F) Amount of SFB 16sRNA in cecum contents of indicated mPCC, Cd3e−/− hosts 8 weeks post T cell transfer (n=5 mice per group, mean±SEM).
(G) Same as (C) with an additional group of RF-housed mPCC, Cd3e−/− mice cohoused with SFB-monocolonized GF mice 3 weeks prior to T cell transfer (RF(SFB)). (n=4 RF and RF(SFB), n=6 RF(MPF) and n=5 MPF, mean±SEM). See also Figure S1.
