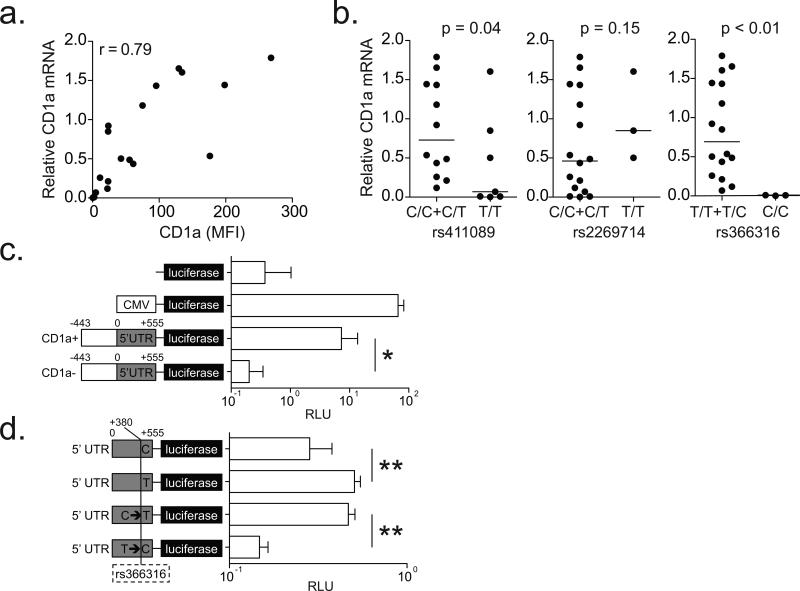
Figure 7. CD1a-deficiency is the result of transcriptional regulation by a SNP in the 5’ UTR.
(a) CD1a mRNA levels were normalized to that of the housekeeping gene glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). Simple linear correlation between relative CD1a mRNA levels and surface protein expression in DCs is shown. (b) Relative CD1a mRNA levels stratified by SNP genotypes are shown with results of one-sided hypothesis testing. (c) HEK293T cells were transfected with firefly luciferase-expressing plasmids (pGL4) under the control of various promoter sequences: none, cytomegalovirus (CMV), 998 bp from CD1a-sufficient (CD1a+), or CD1a-deficient (CD1a-). Cells were co-transfected with Renilla luciferase under a SV40 promoter, and data are reported as relative luciferase units (RLU) which is calculated by dividing the firefly luciferase signal by the Renilla luciferase signal. (d) HEK293T cells were transfected with firefly luciferase-expressing plasmids (pGL4) under the control of 555 bp CD1A 5’ UTR with variants of rs366316: natural C allele, natural T allele, C mutated to T (C→T), or T mutated to C (T→C). All data are representative of two or three independent experiments. * p=0.003 and ** p<0.001 by Welch two sample t-test.