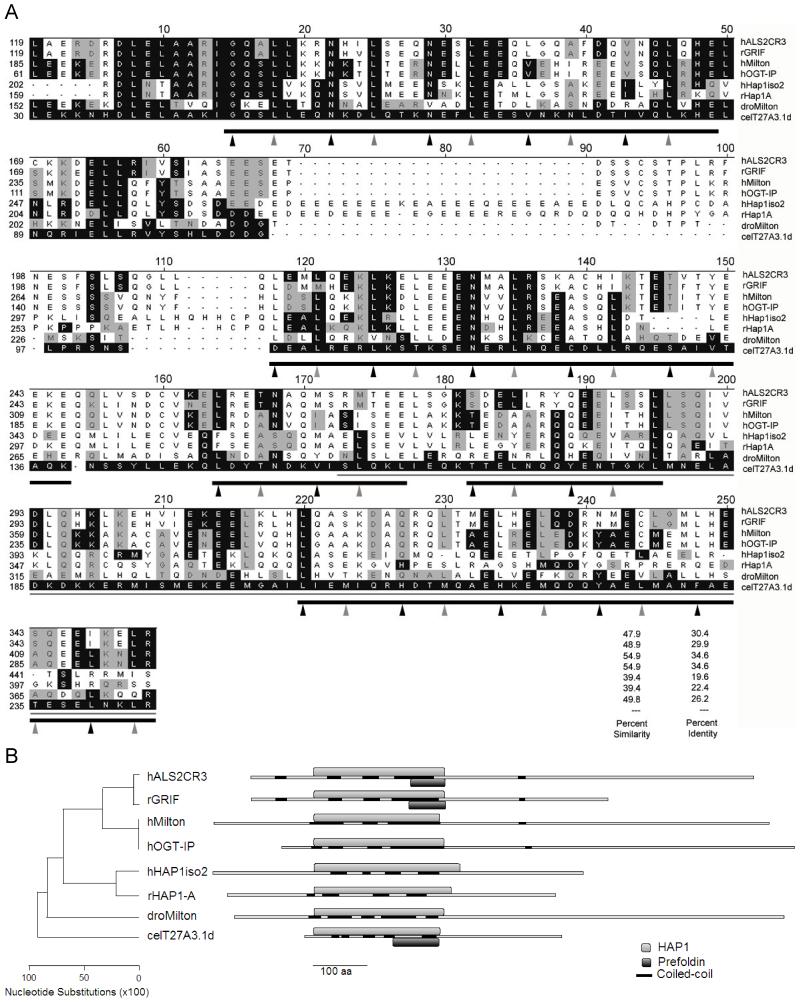
Figure 1. Comparison of an N-terminal fragment of T27A3.1d to the most closely related sequences in the databases.
(A) Clustal W alignment of human ALS2CR3 (hALS2CR3), rat GRIF (rGRIF), human Milton (hMilton), human OGT (hOGT-IP), human HAP1 isoform 2 (hHAP1iso2), rat HAP1-A (rHAP1A), Drosophila Milton (dMilton), and C.elegans T27A3.1d (celT27A3.1d) are shown. The black shaded boxes show identical amino acids and gray shaded boxes show conserved amino acids as they compare to T27A3.1d. The thin gray line represents a putative region of rHAP1-A responsible for binding to htt in yeast. The thick gray lines represent the putative 5 coiled coil regions in T27A3.1d identified by Lupa’s method (Coil at http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/COILS_form.html, window=21). Amino acids in a and d positions in the coiled coil regions are indicated by arrows. T27A3.1d maintains a higher proportion of preferred residues in the a and d positions than rHAP1-A. T27A3.1d more closely resembles human and Drosophila Milton proteins in these a and d positions. Accession numbers are O60296 for hALS2CR3, Q8R2H7 for rGRIF, BAA82994 for hMilton, NP_055780 for hOGT-IP, NP_817084 for hHAP1iso2, AAC52327 for rHAP1A, AY03001 for dMilton, and AAO21402 for T27A3.1d. The percent similarity and identity between T27A3.1d and the other proteins in the alignment are listed.
(B) Schematic of the phylogenetic tree illustrating the relative distance between each of the proteins based on their above shown alignment in DNAStar. Also shown are the relative positions of the aligned N-terminal region shown in A designated as HAP1, the coiled coil domains identified using the Coil online software, and the Prefoldin domain suggested by Pfam.