Figure 6.
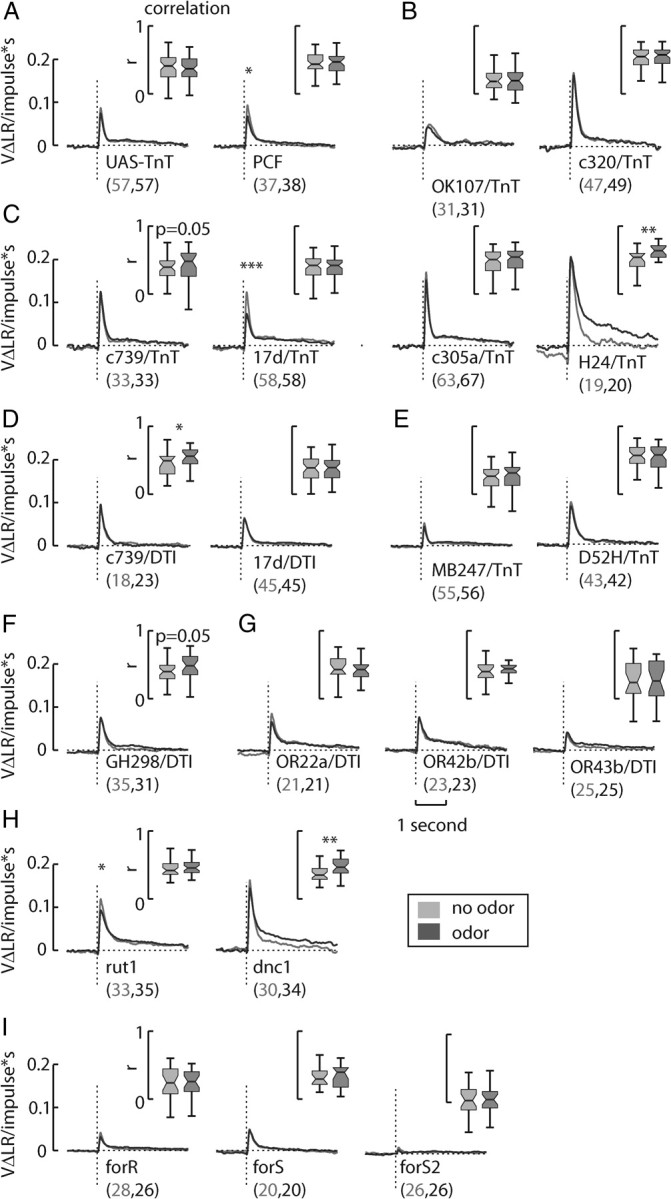
Transgenic sideslip filters. A, A statistically significant decrease in sideslip filter gain was not apparent in the control line UAS-TnT, although such a decrease was detected in the control line PCF. Both control sideslip filters exhibited wild-type dynamics. In contrast, the MB line UAS-TnT+/−; OK107-gal4+/− had reduced sideslip filter with slower dynamics. B, Since the MB line c320-gal4/UAS-TnT had a wild-type sideslip filter, the altered dynamics in the OK107-gal4 line may be due to expression outside the MBs. Expressing TeTxLc in single MB lobes, such as in c739-gal4 (α/β), 17d-gal4 (α/β), c305a-gal4 (α′/β′), and H24-gal4 (γ), did not much alter the overall dynamics of the sideslip response. C, The line 17d-gal4/UAS-TnT appeared to have an enhanced suppression of sideslip filter gain due to odor, and the line H24-gal4 seemed to exhibit an inverted response to odor—an increase of sideslip filter gain. D, Expressing DT with c739-gal4 and 17d-gal4 did not much affect the sideslip filter, by comparison to its effects on the respective yaw filters. E, However, the α/β and γ lobes line UAS-TnT+/−; MB247-gal4+/−had a greatly decreased sideslip filter, perhaps due to expression in the optic ganglia, while the line D52H-gal4; UAS-TnT was wild type. F, Neither the antennal lobe interneuron line GH298-gal4+/−; UAS-DTI+/− or lines expressing DT in OR lines 22a or 42b had abnormal sideslip filters. G, The line OR43b-gal4+/−; UAS-DTI+/− inexplicably had reduced filter gain. H, I, cAMP mutants rut1 and dnc1 both had wild-type sideslip filters (H), while for lines R, S, and S2 all had highly reduced sideslip filters (I). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. An asterisk over the filters indicates a significant difference in peak height. The numbers listed after the name of the line indicates the N in the no odor and odor conditions, respectively.
