Figure 7. Proposed contribution of B cells to immune-mediated bile duct injury in biliary atresia.
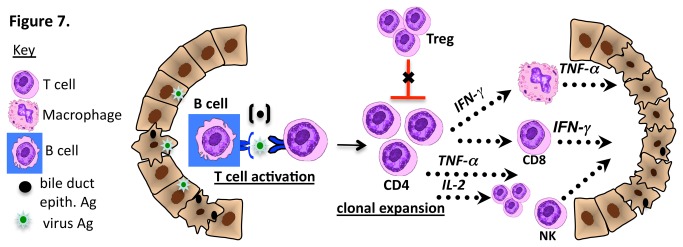
Based on the findings from B cell deficient mice, B cells may function as important antigen presenting cells that present virus or bile duct epithelial antigens (Ag) to naïve CD4+ T cells with subsequent T cell activation and clonal expansion. Activated Th1 cells: secrete IFN-γ leading to macrophage stimulation; stimulate cytotoxic CD8+ T cells; secrete cytotoxic TNF-α and secrete IL-2, leading to further T cell expansion. In addition, B cell activation may inhibit Treg expansion, leading to diminished inhibition of T cell-mediated bile duct injury.
