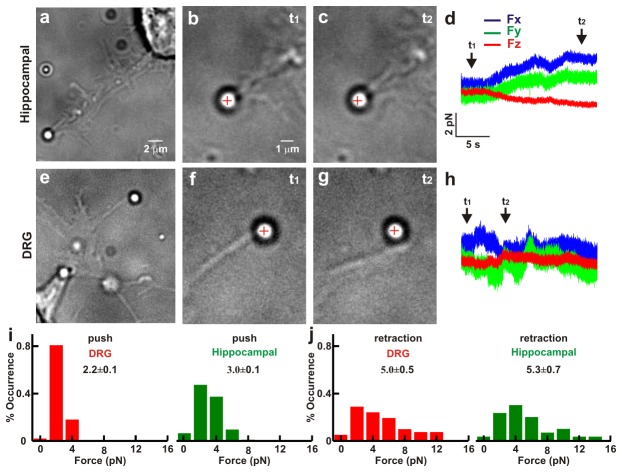
Figure 2. Comparison of the force exerted by filopodia from hippocampal and DRG GCs.
(a) Low resolution image of a bead trapped in front of a filopodium emerging from a GC of hippocampal neuron. (b–c) High resolution images during a push by a filopodium. At t 1 the bead is in the optical trap (b) and at t 2 the filopodium pushes the bead (c). The cross indicates the center of the optical trap. (d) The three components F x, F y, and F z of the force exerted by the filopodium. (e–h) As in (a–d) for a filopodium emerging from a GC of DRG neuron. (i) Histogram of the force measured during a push in DRG (n=58) and hippocampal (n=64) neurons. (j) As in (i) but during retraction (n=31 and n=23 respectively). The trap stiffness is k x,y=0.10, k z=0.03 pN/nm. All values reported in i-j are given as mean ± SE.