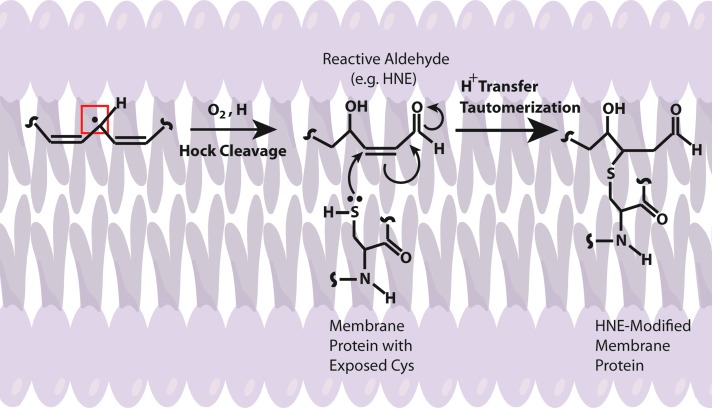
FIG. 4.
Schematic illustration of HNE-modified protein. Upon formation of a radical centered allylic carbon on a fatty acid chain, the lipid may interact with molecular O2 that freely diffuses through the bilayer because of its lack of dipole moment, to initiate the lipid peroxidation process that eventually, by way of a proposed Hock cleavage, generates an α/β unsaturated reactive aldehyde [e.g., 4-hydroxy-nonenal (HNE), malondialdehyde, and acrolein]. Membrane-bound proteins may then, by way of nucleophilic side chains such as Cys, Lys, and His, covalently bind the aldehyde that alters the structure and function of the target protein. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars