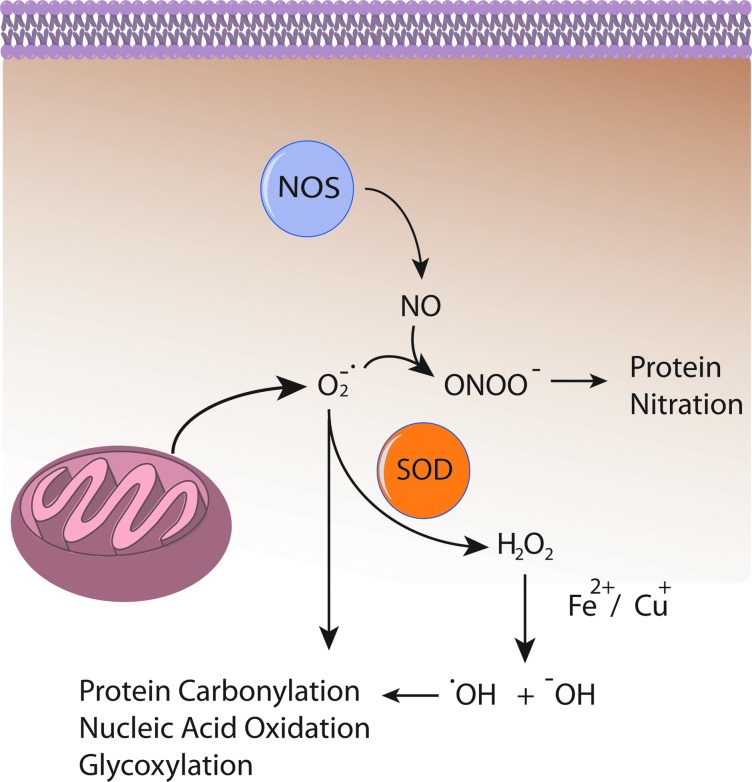
FIG. 5.
Some consequences of elevated ROS and RNS. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) leaked from mitochondria (e.g., O2−•) interact with nitric oxide (NO) produced by nitric oxide synthase (NOS) to produce reactive nitrogen species such as ONOO−, which covalently modify proteins. O2−• can also directly oxidize proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates. O2−• may also be dismutated to H2O2 by superoxide dismutase (SOD) enzymes in an attempt to mitigate O2−• induced damage. However, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in the presence of Fe2+ or Cu+ undergoes Fenton chemistry to produce the reactive ROS •OH and −OH, which also cause protein, nucleic acid, and carbohydrate oxidation. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars