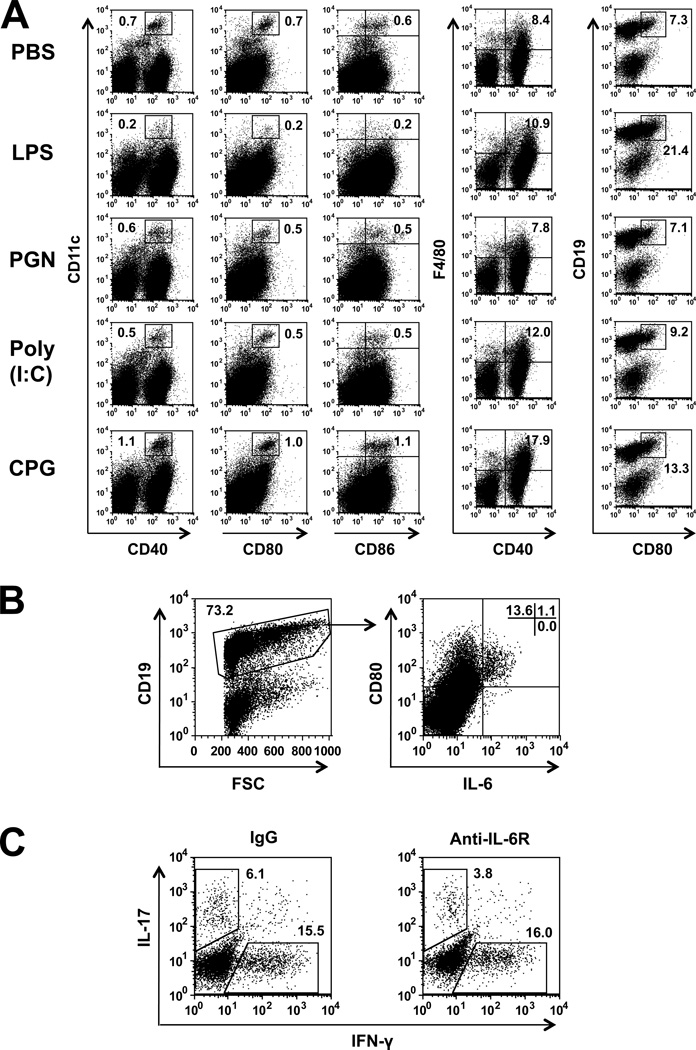
Figure 5.
LPS treatment selectively activates IL-6 producing B-cells. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of spleen cells from recipient mice, 3 days following naïve CD4 cell transfer (on day 0) and treatment with the ligands (day 1). CD11c+ cells were co-stained for CD40, CD80 and CD86; F4/80 were co-stained for CD40; and CD19+ cells were co-stained for CD80. Different patterns of staining by cells treated with the four TLR ligands. Importantly, splenocytes of LPS-treated mice exhibit unique staining pattern, characterized by high expression of CD80 in B cells. (B) Spleen cells from LPS treated mice were gated on CD19+ cells and analyzed for IL-6 production, showing selective production by CD80+ cells. (C) Spleen cells from recipients treated with anti-IL6R Ab or IgG controls were analyzed for intracellular expression of IFN-γ and IL-17. Considerable selective reduction in IL-17 expression by spleen cells of the Ab-treated mice.