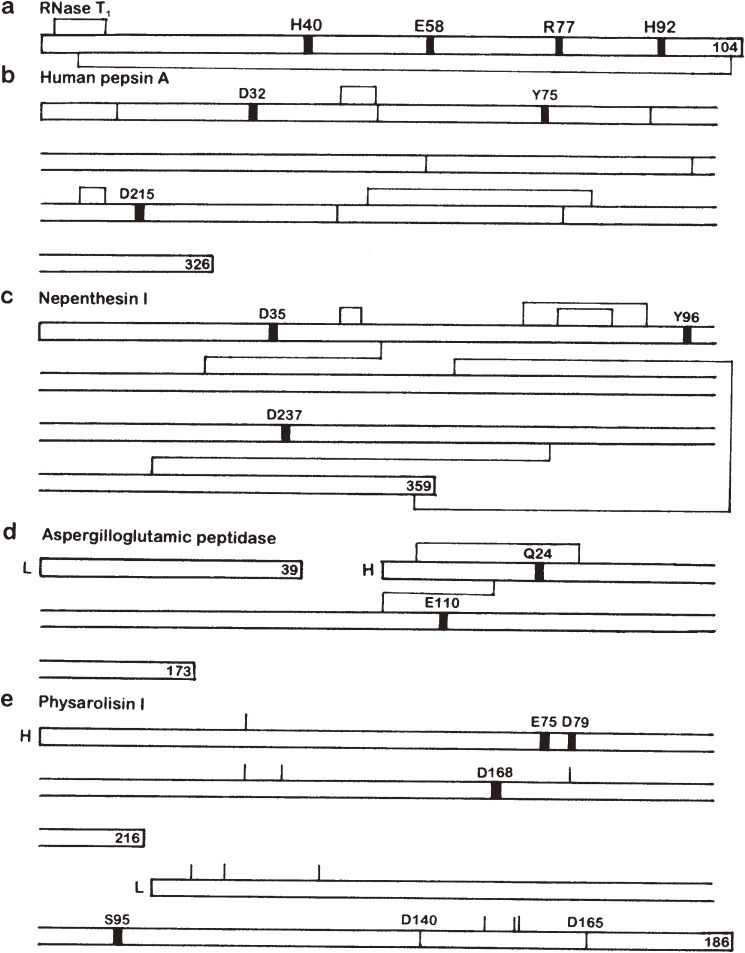
Figure 1.
Gross primary structues and location of the active site residues of some enzymes possessing a catalytic carboxyl group(s). Thick vertical lines in the sequence denote the location of active site residues. Disulfide bonds are shown above and/or below the sequence. L and H stand for L and H chains, respectively. The number at the end of each polypeptide chain indicates the total number of residues. (a) RNase T1. (b) Human pepsin A. The positions corresponding to the intron-exon junctions in the gene are shown with thin vertical lines in the sequence. (c) Nepenthesin I. The disulfide bond pairings were deduced from computer modeling. (d) Aspergilloglutamic peptidase. (e) Physarolisin I. The location of Ca2+-binding Asp residues are also shown with thin vertical lines in the sequence. As the disulfide bond pairings have not been determined, the location of cysteine residues are shown with thin vertical lines above the sequence.