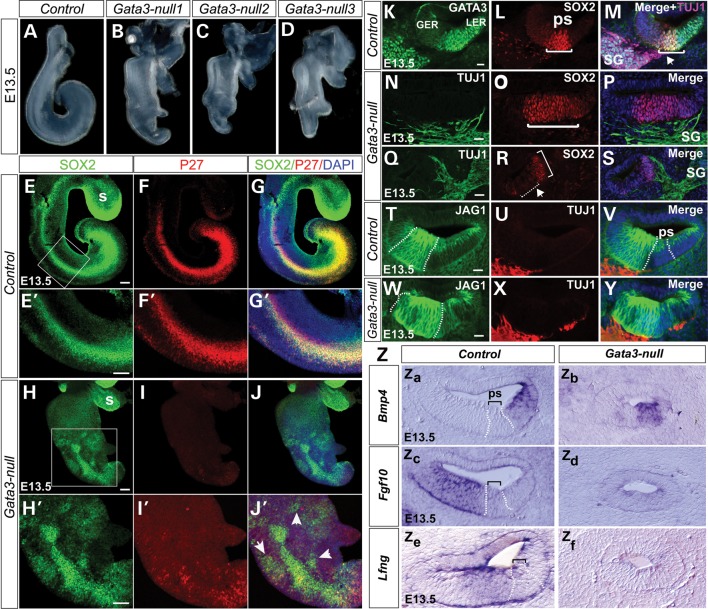
Figure 4.
Gata3 is required for the establishment of the prosensory domain and the axon targeting process of SGNs. (A–D) Compared with the cochlea of wide-type mice (A), the cochleas of Gata3-null mice are shorter with no obvious turn and show some degree of bifurcation at the apex region (B–D). Three representative cochleas of Gata3-null mice are shown. (E–J′) Failure of prosensory domain establishment in Gata-3 null mice at E13.5. Whole mount immunohistochemistry reveals the dramatically decreased expression of SOX and P27kip1 as well as ectopic expression (arrowheads in J’) in the Gata-3 null cochlea. (E′–J′) High magnification of the boxed region in (E)–(J). (K–S) Anti-SOX2 and anti-GATA3 labeling shows the broader (N–P) or ectopic prosensory regions in Gata3-null mice. In addition, compared with the projections of SG specifically to the prosensory domain in wild-type mice (arrow head in M), the projections of SG are not specific in Gata3-null mice (N–P). (T–Y) Immunolabeling shows the altered expression pattern of JAG1 in the Gata3-null cochlea (Z) In situ hybridization analysis of Bmp4 and Fgf10 at E13.5, In Gata3-null mice, the expression of these genes is less defined. In addition, the expression of Fgf10 is down-regulated in Gata3-null mice. GER, greater epithelial ridge; LER, lesser epithelial ridge; ps, prosensory domain; SG, spiral ganglion neurons. s, saccule, Scale bars (E–J′) 100 µm (K–Y) 25 µm.