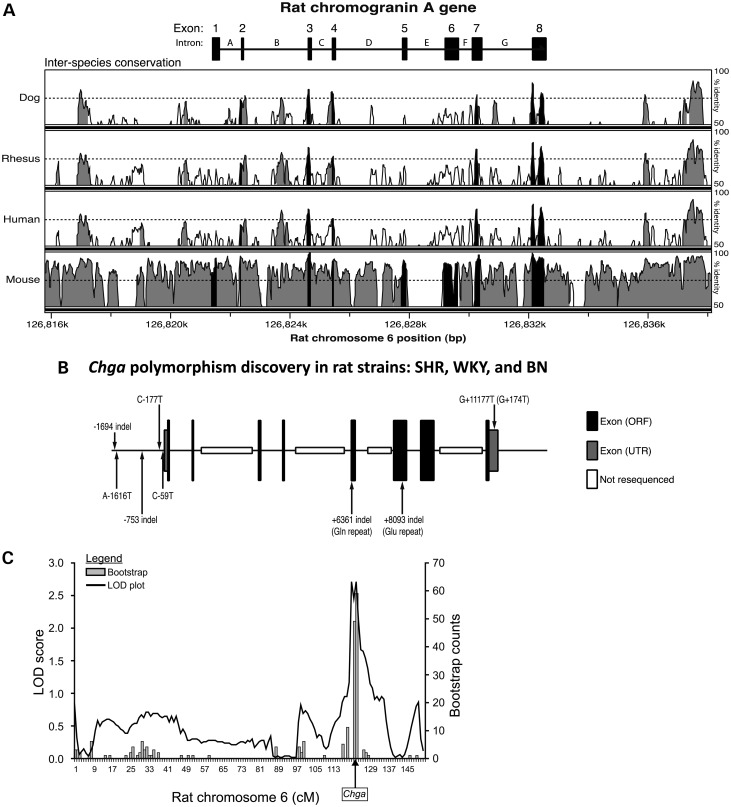
Figure 2.
Chga locus on rat chromosome 6q32: Genomics. Inter-species sequence conservation, systematic polymorphism discovery across strains and cis-QTL. (A) Inter-species conservation at the Chga locus. Conservation of the rat Chga locus across dog, rhesus, human and mouse genomes is presented. Regions of the locus exceeding 70% conservation in a 100 bp sliding window analysis are colored either black (exons) or grey (upstream, intronic or downstream regions). The 70% conservation threshold is indicated with a horizontal dashed line. (B) Polymorphisms discovered through re-sequencing of the rat Chga locus. Results in the SHR, WKY and BN rat strains are also presented. Intronic SNPs and SNPs downstream of the final exon are not displayed. The Chga mRNA cap site (transcriptional start site) was designated as position ‘0’. Base pair position upstream of the cap site (i.e. in the promoter) was numbered negatively in the descending order. Base pair position downstream of the cap site in the exonic and intronic regions was numbered in ascending order. ORF, open reading frame; UTR, untranslated region. (C) The Chga locus as a cis-QTL. Mapping of adrenal Chga protein (by immunoassay) as a quantitative trait in the HXB/BXH RI strains resulted in a significant meiotic recombination (linkage) peak (LOD = 2.58, P = 0.00028) on rat chromosome-6q32 over the Chga locus (shown with an arrow). 2000 bootstraps refined the position of the QTL. The QTL accounted for ∼35% of trait variance. The SHR genotype was directionally associated with increased adrenal Chga protein. The x-axis is displayed in genetic (recombination) units of centimorgans (cM). Genome wide-significance was approached by 2000 permutations, establishing thresholds for significant (LRS = 16.12, LOD = 3.49) and suggestive (LRS = 9.64, LOD = 2.09) linkage.