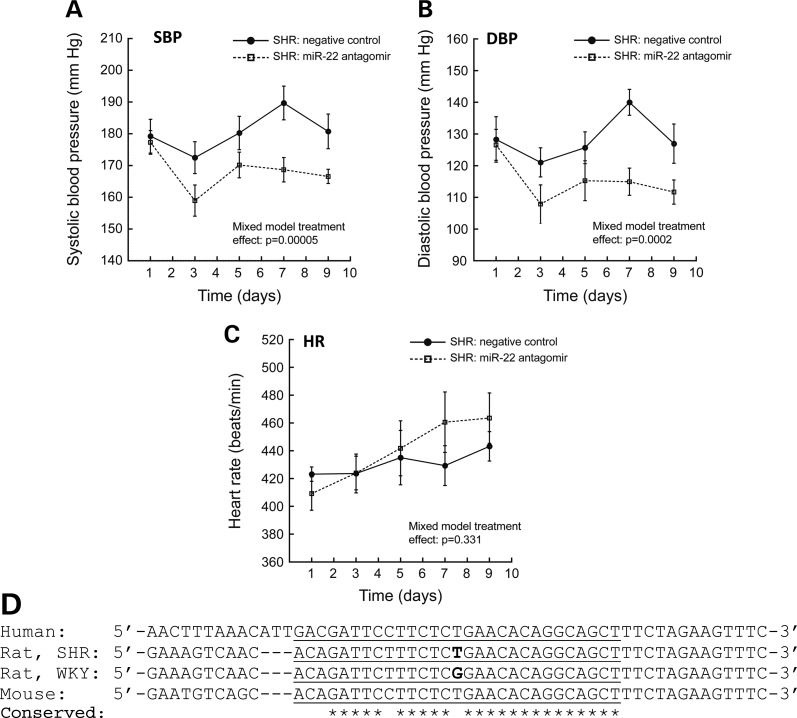
Figure 6.
MicroRNA-22 inhibition in vivo and conservation across species. (A–C) MicroRNA-22 inhibition in vivo: miR-22 antagomir decreases blood pressure in the SHR. SHR were administered either miR-22 antagomir (n = 10) or scrambled sequence negative control (n = 9) via IP injection. Animals received IP doses (at 25 mg/kg) on Days 1, 3, 5, and 7. MicroRNA-22 antagomir treatment significantly reduced both systolic (A) and diastolic (B) blood pressure in the SHR (versus negative control group). Antagomir administration had substantial acute (∼18 mmHg reduction within 48 h) and sustained (∼13 mmHg reduction after 9 days) effects on blood pressure. MicroRNA-22 antagomir administration had no effect on heart rate (C). Data were analyzed with a linear mixed effects model in SPSS. (D) Inter-species conservation of the miR-22 binding site in the 3′-UTR region of the rat Chga locus. The predicted site of miR-22 hybridization (as it would occur in transcribed Chga mRNA) is underlined in the DNA sequence of the Chga locus. Location of the SHR/WKY G + 174T SNP (SHR allele = ‘T’; WKY allele = ‘G’) is shown in bold text. Individual bases conserved across human, rat and mouse are indicated with *. The miR-22 binding site is well conserved, indicating its likelihood of miR-22 regulation of CHGA in humans. Note that WKY and BN 3′-UTR sequences are identical.